Mutant huntingtin alters cell fate in response to microtubule depolymerization via the GEF-H1-RhoA-ERK pathway
- PMID: 20858895
- PMCID: PMC2988350
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.125542
Mutant huntingtin alters cell fate in response to microtubule depolymerization via the GEF-H1-RhoA-ERK pathway
Abstract
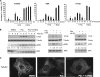
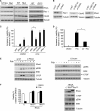
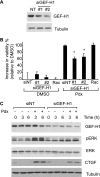
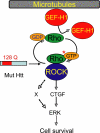
Cellular responses to drug treatment show tremendous variations. Elucidating mechanisms underlying these variations is critical for predicting therapeutic responses and developing personalized therapeutics. Using a small molecule screening approach, we discovered how a disease causing allele leads to opposing cell fates upon pharmacological perturbation. Diverse microtubule-depolymerizing agents protected mutant huntingtin-expressing cells from cell death, while being toxic to cells lacking mutant huntingtin or those expressing wild-type huntingtin. Additional neuronal cell lines and primary neurons from Huntington disease mice also showed altered survival upon microtubule depolymerization. Transcription profiling revealed that microtubule depolymerization induced the autocrine growth factor connective tissue growth factor and activated ERK survival signaling. The genotype-selective rescue was dependent upon increased RhoA protein levels in mutant huntingtin-expressing cells, because inhibition of RhoA, its downstream effector, Rho-associated kinase (ROCK), or a microtubule-associated RhoA activator, guanine nucleotide exchange factor-H1 (GEF-H1), all attenuated the rescue. Conversely, RhoA overexpression in cells lacking mutant huntingtin conferred resistance to microtubule-depolymerizer toxicity. This study elucidates a novel pathway linking microtubule stability to cell survival and provides insight into how genetic context can dramatically alter cellular responses to pharmacological interventions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The epidermal growth factor receptor mediates tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced activation of the ERK/GEF-H1/RhoA pathway in tubular epithelium.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 18;286(11):9268-79. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.179903. Epub 2011 Jan 6. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21212278 Free PMC article.
-
Role of guanine nucleotide exchange factor-H1 in complement-mediated RhoA activation in glomerular epithelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 14;289(7):4206-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.506816. Epub 2013 Dec 19. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24356971 Free PMC article.
-
GEF-H1 couples nocodazole-induced microtubule disassembly to cell contractility via RhoA.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 May;19(5):2147-53. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-12-1269. Epub 2008 Feb 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18287519 Free PMC article.
-
[Huntington's disease: intracellular signaling pathways and neuronal death].J Soc Biol. 2005;199(3):247-51. doi: 10.1051/jbio:2005026. J Soc Biol. 2005. PMID: 16471265 Review. French.
-
RhoA Signaling in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Cells. 2022 May 1;11(9):1520. doi: 10.3390/cells11091520. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563826 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanical Role of Nesprin-1-Mediated Nucleus-Actin Filament Binding in Cyclic Stretch-Induced Fibroblast Elongation.Cell Mol Bioeng. 2017 Apr 10;10(4):327-338. doi: 10.1007/s12195-017-0487-6. eCollection 2017 Aug. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2017. PMID: 31719867 Free PMC article.
-
Regulators of Rho GTPases in the Nervous System: Molecular Implication in Axon Guidance and Neurological Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 25;20(6):1497. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061497. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30934641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of cell cycle arrest by increasing GTP‑RhoA levels via Taxol‑induced microtubule polymerization in renal cell carcinoma.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Jun;15(6):4273-4279. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6543. Epub 2017 May 3. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28487984 Free PMC article.
-
MAP kinase phosphatase 1 (MKP-1/DUSP1) is neuroprotective in Huntington's disease via additive effects of JNK and p38 inhibition.J Neurosci. 2013 Feb 6;33(6):2313-25. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4965-11.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23392662 Free PMC article.
-
A novel target for Huntington's disease: ERK at the crossroads of signaling. The ERK signaling pathway is implicated in Huntington's disease and its upregulation ameliorates pathology.Bioessays. 2012 Feb;34(2):142-8. doi: 10.1002/bies.201100116. Bioessays. 2012. PMID: 22334892 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

