The methanogen-specific transcription factor MsvR regulates the fpaA-rlp-rub oxidative stress operon adjacent to msvR in Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus
- PMID: 20851905
- PMCID: PMC2976444
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00816-10
The methanogen-specific transcription factor MsvR regulates the fpaA-rlp-rub oxidative stress operon adjacent to msvR in Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus
Abstract
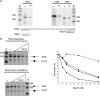
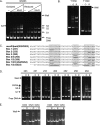
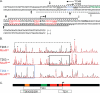
Methanogens represent some of the most oxygen-sensitive organisms in laboratory culture. Recent studies indicate that they have developed mechanisms to deal with brief oxygen exposure. MsvR is a transcriptional regulator that has a domain architecture unique to a select group of methanogens. Here, runoff in vitro transcription assays were used to demonstrate that MsvR regulates transcription of the divergently transcribed fpaA-rlp-rub operon in Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus in addition to transcription from its own promoter. The protein products of the fpaA-rlp-rub operon have previously been implicated in oxidative stress responses in M. thermautotrophicus. Additionally, electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs) and DNase I footprinting were used to confirm a binding site inferred by bioinformatic analysis. Sequence mutations within these binding sites did not significantly alter EMSA shifting patterns on longer templates but did on shorter 50-bp fragments encompassing only the region containing the binding sites. Footprinting confirmed that the regions protected for the longer mutant templates are at different positions within the intergenic region compared to those seen in the intact intergenic region. Oxidized and reduced preparations of MsvR demonstrated different EMSA binding patterns and regions of protection on the intergenic sequence, suggesting that MsvR may play a role in detecting the redox state of the cell.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Redox-sensitive DNA binding by homodimeric Methanosarcina acetivorans MsvR is modulated by cysteine residues.BMC Microbiol. 2013 Jul 16;13:163. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-163. BMC Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23865844 Free PMC article.
-
Specific DNA binding of a potential transcriptional regulator, inosine 5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase-related protein VII, to the promoter region of a methyl coenzyme m reductase I-encoding operon retrieved from Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus strain DeltaH.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Oct;74(20):6239-47. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02155-07. Epub 2008 Aug 29. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18757575 Free PMC article.
-
ZntR is an autoregulatory protein and negatively regulates the chromosomal zinc resistance operon znt of Staphylococcus aureus.Mol Microbiol. 1999 Jul;33(1):200-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01466.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10411736
-
Regulators of the Bacillus subtilis cydABCD operon: identification of a negative regulator, CcpA, and a positive regulator, ResD.J Bacteriol. 2007 May;189(9):3348-58. doi: 10.1128/JB.00050-07. Epub 2007 Feb 23. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17322317 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional activation of the catechol and chlorocatechol operons: variations on a theme.Gene. 1998 Nov 26;223(1-2):257-67. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(98)00366-7. Gene. 1998. PMID: 9858745 Review.
Cited by
-
TrmB Family Transcription Factor as a Thiol-Based Regulator of Oxidative Stress Response.mBio. 2022 Aug 30;13(4):e0063322. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00633-22. Epub 2022 Jul 20. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35856564 Free PMC article.
-
Redox-sensitive DNA binding by homodimeric Methanosarcina acetivorans MsvR is modulated by cysteine residues.BMC Microbiol. 2013 Jul 16;13:163. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-163. BMC Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23865844 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Stress Proteins in Haloarchaea and Their Adaptive Response to Environmental Shifts.Biomolecules. 2020 Sep 29;10(10):1390. doi: 10.3390/biom10101390. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33003558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel CO-responsive transcriptional regulator and enhanced H2 production by an engineered Thermococcus onnurineus NA1 strain.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Mar;81(5):1708-14. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03019-14. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25548050 Free PMC article.
-
Negative effect of glucose on ompA mRNA stability: a potential role of cyclic AMP in the repression of hfq in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2011 Oct;193(20):5833-40. doi: 10.1128/JB.05359-11. Epub 2011 Aug 12. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21840983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Bae, J.-B., J.-H. Park, M.-Y. Hahn, M.-S. Kim, and J.-H. Roe. 2004. Redox-dependent changes in RsrA, an anti-sigma factor in Streptomyces coelicolor: zinc release and disulfide bond formation. J. Mol. Biol. 335:425-435. - PubMed
-
- Deppenmeier, U. 2002. The unique biochemistry of methanogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 71:223-283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

