Analysis and characterization of the genes encoding the Dicer and Argonaute proteins of Schistosoma japonicum
- PMID: 20849617
- PMCID: PMC2949827
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-3305-3-90
Analysis and characterization of the genes encoding the Dicer and Argonaute proteins of Schistosoma japonicum
Abstract
Background: The Dicer and Argonaute(AGO) proteins within the small RNA regulatory pathways (SRRPs) play an indispensable role in regulation of gene expression. In this study, we analyzed two genes, Dicer and Argonaute, from Schistosoma japonicum, along with their expression through a combination of bioinformatics and experimental approaches.
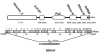
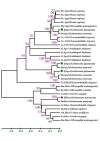
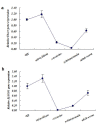
Results: Our results indicate that one Dicer and four Argonaute genes exist in Schistosoma japonicum, termed SjDicer and SjAGO1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively. SjDicer encodes 2590 amino acid residues that contains 5 conserved domains, including one amino-terminal helicase domain, one PAZ (Piwi-Argonaut-Zwille) domain, two RNAse III domains, and one dsRNA-binding domain. SjAGO1, 2, and 3 encode 1009, 945, and 904 amino acid residues, respectively, all of which contain PAZ and PIWI domains. In addition, we analyzed the expression profiles of SjDicer and SjAGO1 genes by qRT-PCR in eggs, miracidium, cercariae, schistosomula, and adult worms. Results showed consistent expression of both SjDicer and SjAGO1 in different stages; however, their expression levels were stage-dependent, with the highest being in the miracidium stage.
Conclusions: This study provided the sequence of the Dicer and Ago genes of S. japonicum and their expression profiles which are essential for further investigation of functions of miRNA in Schistosoma japonicum.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular cloning and expression profiles of Argonaute proteins in Schistosoma japonicum.Parasitol Res. 2010 Sep;107(4):889-99. doi: 10.1007/s00436-010-1946-3. Epub 2010 Jun 26. Parasitol Res. 2010. PMID: 20582438
-
Cloning and characterization of a bone morphogenetic protein homologue of Schistosoma japonicum.Exp Parasitol. 2013 Sep;135(1):64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2013.05.016. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Exp Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23756146
-
Genetic Insight into the Domain Structure and Functions of Dicer-Type Ribonucleases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 9;22(2):616. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020616. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33435485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prokaryotic homologs of Argonaute proteins are predicted to function as key components of a novel system of defense against mobile genetic elements.Biol Direct. 2009 Aug 25;4:29. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-4-29. Biol Direct. 2009. PMID: 19706170 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of RNase III action: how dicer dices.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;320:99-116. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-75157-1_5. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18268841 Review.
Cited by
-
Chromatin structural changes around satellite repeats on the female sex chromosome in Schistosoma mansoni and their possible role in sex chromosome emergence.Genome Biol. 2012 Feb 29;13(2):R14. doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-2-r14. Genome Biol. 2012. PMID: 22377319 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Nanos and Ago Genes Expression in the Germinative Cells Isolated from Germinal Layer and the Neck Region of Echinococcus granulosus.Iran J Parasitol. 2024 Apr-Jun;19(2):131-139. doi: 10.18502/ijpa.v19i2.15849. Iran J Parasitol. 2024. PMID: 39011528 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs Are Involved in the Regulation of Ovary Development in the Pathogenic Blood Fluke Schistosoma japonicum.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Feb 12;12(2):e1005423. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005423. eCollection 2016 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 26871705 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the functional biology of schistosomes.Parasit Vectors. 2011 Oct 20;4:203. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-4-203. Parasit Vectors. 2011. PMID: 22013990 Free PMC article.
-
A deep analysis of the small non-coding RNA population in Schistosoma japonicum eggs.PLoS One. 2013 May 14;8(5):e64003. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064003. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23691136 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keene KM, Foy BD, Sanchez-Vargas I, Beaty BJ, Blair CD, Olson KE. RNA interference acts as a natural antiviral response to O'nyong-nyong virus (Alphavirus; Togaviridae) infection of Anopheles gambiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101(49):17240–17245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406983101. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

