Bone morphogenetic protein 4 enhances canonical transient receptor potential expression, store-operated Ca2+ entry, and basal [Ca2+]i in rat distal pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 20844246
- PMCID: PMC3006336
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00040.2010
Bone morphogenetic protein 4 enhances canonical transient receptor potential expression, store-operated Ca2+ entry, and basal [Ca2+]i in rat distal pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells
Abstract
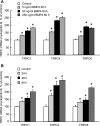
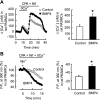
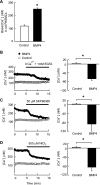
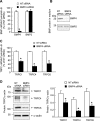
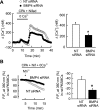
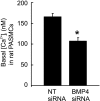
Recent advances have identified an important role of bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) in pulmonary vascular remodeling, yet the underlying mechanisms remain largely unexplored. We have previously found that Ca(2+) influx through store-operated calcium channels (SOCC), which are mainly thought to be composed of canonical transient receptor potential (TRPC) proteins, likely contribute to the pathogenic development of chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. In this study, we investigated the effect of BMP4 on expression of TRPC and store-operated Ca(2+) entry (SOCE) in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMCs). Real-time quantitative PCR and Western blotting revealed that treatment with BMP4 (50 ng/ml, 60 h) increased TRPC1, TRPC4, and TRPC6 mRNA and protein expression in growth-arrested rat distal PASMCs. Moreover, in comparison to vehicle control, cells treated with BMP4 also exhibited enhanced SOCE, and elevated basal intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)) as determined by fluorescent microscopy using the Ca(2+) indicator Fura-2 AM. Perfusing cells with Ca(2+)-free Krebs-Ringer bicarbonate solution (KRBS) or KRBS containing SOCC antagonists SKF-96365 or NiCl(2) attenuated the increases in basal [Ca(2+)](i) caused by BMP4. Specific knockdown of BMP4 by small interference RNA significantly decreased the mRNA and protein expression of TRPC1, TRPC4, and TRPC6 and reduced SOCE and basal [Ca(2+)](i) in serum-stimulated PASMCs. We conclude that BMP4 regulates calcium signaling in PASMCs likely via upregulation of TRPC expression, leading to enhanced SOCE and basal [Ca(2+)](i) in PASMCs, and by this mechanism contributes to pulmonary vascular remodeling during pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Figures
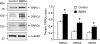
Similar articles
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 decreases TRPC expression, store-operated Ca(2+) entry, and basal [Ca(2+)]i in rat distal pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 May 1;304(9):C833-43. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00036.2012. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23447035 Free PMC article.
-
BMP4 increases canonical transient receptor potential protein expression by activating p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Aug;49(2):212-20. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0051OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23526217 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic hypoxia-induced upregulation of store-operated and receptor-operated Ca2+ channels in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells: a novel mechanism of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension.Circ Res. 2004 Sep 3;95(5):496-505. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000138952.16382.ad. Epub 2004 Jul 15. Circ Res. 2004. PMID: 15256480
-
The Molecular Heterogeneity of Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry in Vascular Endothelial Cells: The Different roles of Orai1 and TRPC1/TRPC4 Channels in the Transition from Ca2+-Selective to Non-Selective Cation Currents.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 7;24(4):3259. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043259. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Store-operated calcium entry: Pivotal roles in renal physiology and pathophysiology.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Feb;246(3):305-316. doi: 10.1177/1535370220975207. Epub 2020 Nov 29. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 33249888 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 decreases TRPC expression, store-operated Ca(2+) entry, and basal [Ca(2+)]i in rat distal pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 May 1;304(9):C833-43. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00036.2012. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23447035 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate inhibits canonical transient receptor potential expression in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle from pulmonary hypertensive rats.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Jan;48(1):125-34. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0071OC. Epub 2012 Oct 11. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23065131 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and clinical analysis of TRPC6 and AGTR1 genes in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015 Jan 21;10:1. doi: 10.1186/s13023-014-0216-3. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015. PMID: 25603901 Free PMC article.
-
Noggin inhibits hypoxia-induced proliferation by targeting store-operated calcium entry and transient receptor potential cation channels.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015 Jun 1;308(11):C869-78. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00349.2014. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25740156 Free PMC article.
-
NOX4 mediates BMP4-induced upregulation of TRPC1 and 6 protein expressions in distal pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 9;9(9):e107135. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107135. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25203114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atkinson C, Stewart S, Upton PD, Machado R, Thomson JR, Trembath RC, Morrell NW. Primary pulmonary hypertension is associated with reduced pulmonary vascular expression of type II bone morphogenetic protein receptor. Circulation 105: 1672–1678, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ. Calcium signalling and cell proliferation. Bioessays 17: 491–500, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 517–529, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Boulay G, Zhu X, Peyton M, Jiang M, Hurst R, Stefani E, Birnbaumer L. Cloning and expression of a novel mammalian homolog of Drosophila transient receptor potential (Trp) involved in calcium entry secondary to activation of receptors coupled by the Gq class of G protein. J Biol Chem 272: 29672–29680, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Deng Z, Morse JH, Slager SL, Cuervo N, Moore KJ, Venetos G, Kalachikov S, Cayanis E, Fischer SG, Barst RJ, Hodge SE, Knowles JA. Familial primary pulmonary hypertension (gene PPH1) is caused by mutations in the bone morphogenetic protein receptor-II gene. Am J Hum Genet 67: 737–744, 2000 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

