Induction of interleukin-23 p19 by serum amyloid A (SAA) in rheumatoid synoviocytes
- PMID: 20840651
- PMCID: PMC2996591
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04242.x
Induction of interleukin-23 p19 by serum amyloid A (SAA) in rheumatoid synoviocytes
Abstract
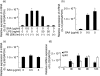
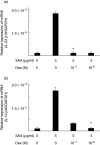
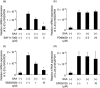
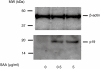
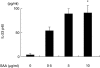
In this study, we investigated the roles of serum amyloid A (SAA) in T helper 17 (Th17)-related cytokine induction in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synoviocytes. Synoviocytes isolated from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients were stimulated with recombinant SAA and IL-23 expression was investigated using reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and Western blot. The involvement of mitogen-activated protein kineases (MAPKs) and nuclear factor (NF)-κB in SAA-induced interleukin (IL)-23 p19 expression was investigated using pharmacological inhibitors. In RA synoviocytes, SAA induced the expression of IL-23 p19 and p40 mRNA expression. The SAA-stimulated expression of p19 was rapid (< 3 h), and insensitive to polymyxin B treatment. This SAA-stimulated expression of IL-23 p19 was inhibited completely by inhibitors of NF-κB, p38MAPK and dexamethasone. Interestingly, the SAA-induced IL-23, p19 and p40 production was accompanied by enhanced expression of IL-1β, but not transforming growth factor-β. These results indicate that SAA is a significant inducer of IL-23 and IL-1β in RA synoviocytes and potentially activates the IL-23/IL-17 pathway in the RA synovium. Our data present a novel interaction between inflammation and autoimmunity by an acute-phase protein.
© 2010 The Authors; Clinical and Experimental Immunology © 2010 British Society for Immunology.
Figures

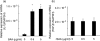
Similar articles
-
Interleukin (IL)-23 p19 expression induced by IL-1beta in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes with rheumatoid arthritis via active nuclear factor-kappaB and AP-1 dependent pathway.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007 Aug;46(8):1266-73. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kem055. Epub 2007 Jun 14. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007. PMID: 17569750
-
Serum amyloid A protein stimulates CCL20 production in rheumatoid synoviocytes.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009 Jul;48(7):741-7. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kep089. Epub 2009 May 15. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009. PMID: 19447772
-
Abundant expression of the interleukin (IL)23 subunit p19, but low levels of bioactive IL23 in the rheumatoid synovium: differential expression and Toll-like receptor-(TLR) dependent regulation of the IL23 subunits, p19 and p40, in rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2009 Jan;68(1):143-50. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.082081. Epub 2008 Feb 14. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009. PMID: 18276743
-
Interleukin-23 as a potential therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Feb;361(1-2):243-8. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-1109-6. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22012611 Review.
-
Serum amyloid A-A potential therapeutic target for hyper-inflammatory syndrome associated with COVID-19.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 16;10:1135695. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1135695. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37007776 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Etiologies of Sarcoidosis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2015 Aug;49(1):6-18. doi: 10.1007/s12016-015-8481-z. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25771769 Review.
-
Prostaglandin E2-induced IL-23p19 subunit is regulated by cAMP-responsive element-binding protein and C/AATT enhancer-binding protein β in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells.J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 26;287(44):36922-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.402958. Epub 2012 Sep 12. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22977257 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of IL-23 in rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2011 Aug;30(8):1135-6. doi: 10.1007/s10067-011-1801-7. Epub 2011 Jun 18. Clin Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21681645 No abstract available.
-
The cytokine-serum amyloid A-chemokine network.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016 Aug;30:55-69. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.12.010. Epub 2015 Dec 28. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016. PMID: 26794452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mucosal candidiasis elicits NF-κB activation, proinflammatory gene expression and localized neutrophilia in zebrafish.Dis Model Mech. 2013 Sep;6(5):1260-70. doi: 10.1242/dmm.012039. Epub 2013 May 29. Dis Model Mech. 2013. PMID: 23720235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fouser LA, Wright JF, Dunussi-Joannopoulos K, Collins M. Th17 cytokines and their emerging roles in inflammation and autoimmunity. Immunol Rev. 2008;226:87–102. - PubMed
-
- Chabaud M, Durand JM, Buchs N, et al. Human interleukin-17: a T cell-derived proinflammatory cytokine produced by the rheumatoid synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:963–70. - PubMed
-
- Annunziato F, Cosmi L, Liotta F, Maggi E, Romagnani S. Type 17 T helper cells-origins, features and possible roles in rheumatic disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009;5:325–31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

