The intrinsic innervation of the lung is derived from neural crest cells as shown by optical projection tomography in Wnt1-Cre;YFP reporter mice
- PMID: 20840354
- PMCID: PMC3039178
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2010.01295.x
The intrinsic innervation of the lung is derived from neural crest cells as shown by optical projection tomography in Wnt1-Cre;YFP reporter mice
Abstract
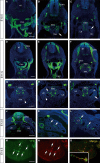
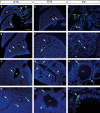
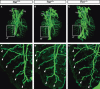
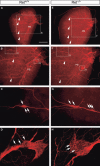
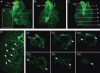
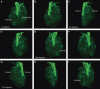
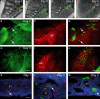
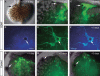
Within the embryonic lung, intrinsic nerve ganglia, which innervate airway smooth muscle, are required for normal lung development and function. We studied the development of neural crest-derived intrinsic neurons within the embryonic mouse lung by crossing Wnt1-Cre mice with R26R-EYFP reporter mice to generate double transgenic mice that express yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) in all neural crest cells (NCCs) and their derivatives. In addition to utilizing conventional immunohistochemistry on frozen lung sections, the complex organization of lung innervation was visualized in three dimensions by combining the genetic labelling of NCCs with optical projection tomography, a novel imaging technique that is particularly useful for the 3D examination of developing organs within embryos. YFP-positive NCCs migrated into the mouse lung from the oesophagus region at embryonic day 10.5. These cells subsequently accumulated around the bronchi and epithelial tubules of the lung and, as shown by 3D lung reconstructions with optical projection tomography imaging, formed an extensive, branching network in association with the developing airways. YFP-positive cells also colonized lung maintained in organotypic culture, and responded in a chemoattractive manner to the proto-oncogene, rearranged during transfection (RET) ligand, glial-cell-line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), suggesting that the RET signalling pathway is involved in neuronal development within the lung. However, when the lungs of Ret(-/-) and Gfrα1(-/-) embryos, deficient in the RET receptor and GDNF family receptor α 1 (GFRα1) co-receptor respectively, were examined, no major differences in the extent of lung innervation were observed. Our findings demonstrate that intrinsic neurons of the mouse lung are derived from NCCs and that, although implicated in the development of these cells, the role of the RET signalling pathway requires further investigation.
© 2010 The Authors. Journal of Anatomy © 2010 Anatomical Society of Great Britain and Ireland.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of the neural crest-derived intrinsic innervation of the human lung.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008 Mar;38(3):269-75. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0246OC. Epub 2007 Sep 20. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 17884989
-
Prokineticin-1 (Prok-1) works coordinately with glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) to mediate proliferation and differentiation of enteric neural crest cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Mar;1783(3):467-78. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.09.005. Epub 2007 Oct 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18006159
-
Expression of the GDNF receptors ret and GFRalpha1 in the developing avian enteric nervous system.J Comp Neurol. 1999 Nov 15;414(2):193-211. J Comp Neurol. 1999. PMID: 10516591
-
Enteric neural crest-derived cells and neural stem cells: biology and therapeutic potential.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2004 Apr;16 Suppl 1:3-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-3150.2004.00466.x. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2004. PMID: 15065996 Review.
-
Neurotrophin-3 in the development of the enteric nervous system.Prog Brain Res. 2004;146:243-63. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(03)46016-0. Prog Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 14699968 Review.
Cited by
-
Vascularisation is not necessary for gut colonisation by enteric neural crest cells.Dev Biol. 2014 Jan 15;385(2):220-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.11.007. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24262984 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of respiratory innervation during embryonic development.Organogenesis. 2013 Jul-Sep;9(3):194-8. doi: 10.4161/org.24842. Epub 2013 May 14. Organogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23974176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Models to Study Human Lung Development, Disease and Homeostasis.Physiology (Bethesda). 2017 May;32(3):246-260. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00041.2016. Physiology (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28404740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation and culture of neural crest cells from embryonic murine neural tube.J Vis Exp. 2012 Jun 2;(64):e4134. doi: 10.3791/4134. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 22688801 Free PMC article.
-
Migration pathways of sacral neural crest during development of lower urogenital tract innervation.Dev Biol. 2017 Sep 1;429(1):356-369. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.04.011. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28449850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amiel J, Sproat-Emison E, Garcia-Barcelo M, et al. Hirschsprung disease, associated syndromes and genetics: a review. J Med Genet. 2008;45:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Barlow AJ, Wallace AS, Thapar N, et al. Critical numbers of neural crest cells are required in the pathways from the neural tube to the foregut to ensure complete enteric nervous system formation. Development. 2008;135:1681–1691. - PubMed
-
- Burns AJ. Migration of neural crest-derived enteric nervous system precursor cells to and within the gastrointestinal tract. Int J Dev Biol. 2005;49:143–150. - PubMed
-
- Burns AJ, Delalande JM. Neural crest cell origin for intrinsic ganglia of the developing chicken lung. Dev Biol. 2005;277:63–79. - PubMed
-
- Burns AJ, Le Douarin NM. The sacral neural crest contributes neurons and glia to the post-umbilical gut: spatiotemporal analysis of the development of the enteric nervous system. Development. 1998;125:4335–4347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

