Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in ginger (Zingiber officinale)
- PMID: 20837112
- PMCID: PMC3018740
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fitote.2010.09.004
Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in ginger (Zingiber officinale)
Abstract
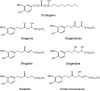
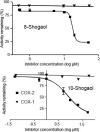
Ginger roots have been used to treat inflammation and have been reported to inhibit cyclooxygenase (COX). Ultrafiltration liquid chromatography mass spectrometry was used to screen a chloroform partition of a methanol extract of ginger roots for COX-2 ligands, and 10-gingerol, 12-gingerol, 8-shogaol, 10-shogaol, 6-gingerdione, 8-gingerdione, 10-gingerdione, 6-dehydro-10-gingerol, 6-paradol, and 8-paradol bound to the enzyme active site. Purified 10-gingerol, 8-shogaol and 10-shogaol inhibited COX-2 with IC(50) values of 32 μM, 17.5 μM and 7.5 μM, respectively. No inhibition of COX-1 was detected. Therefore, 10-gingerol, 8-shogaol and 10-shogaol inhibit COX-2 but not COX-1, which can explain, in part, the anti-inflammatory properties of ginger.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Blood-brain barrier permeability study of ginger constituents.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020 Jan 5;177:112820. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2019.112820. Epub 2019 Aug 19. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020. PMID: 31476432
-
Optimization protocol for the extraction of 6-gingerol and 6-shogaol from Zingiber officinale var. rubrum Theilade and improving antioxidant and anticancer activity using response surface methodology.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Jul 30;15:258. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0718-0. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 26223685 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of [6]-gingerol, [8]-gingerol, [10]-gingerol and [6]-shogaol.J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Feb 3;127(2):515-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.10.004. Epub 2009 Oct 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19833188
-
Revisiting the therapeutic potential of gingerols against different pharmacological activities.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Apr;396(4):633-647. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02372-7. Epub 2022 Dec 31. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36585999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective and therapeutic potential of ginger (Zingiber officinale) extract and [6]-gingerol in cancer: A comprehensive review.Phytother Res. 2018 Oct;32(10):1885-1907. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6134. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Phytother Res. 2018. PMID: 30009484 Review.
Cited by
-
Phytotherapy in Integrative Oncology-An Update of Promising Treatment Options.Molecules. 2022 May 17;27(10):3209. doi: 10.3390/molecules27103209. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35630688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginger extract versus Loratadine in the treatment of allergic rhinitis: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Apr 20;20(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-2875-z. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32312261 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of analytical techniques for the identification of bioactive compounds from natural products.Nat Prod Rep. 2016 Oct 28;33(10):1131-45. doi: 10.1039/c6np00016a. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Nat Prod Rep. 2016. PMID: 27367973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) in the Prevention of Ageing and Degenerative Diseases: Review of Current Evidence.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Aug 20;2019:5054395. doi: 10.1155/2019/5054395. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31531114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Benjakul Remedy Extract for Treating Primary Osteoarthritis of Knee Compared with Diclofenac: Double Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:9593580. doi: 10.1155/2017/9593580. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 29234447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yokoyama C, Tanabe T T. Cloning of human gene encoding prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase and primary structure of the enzyme. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989;165:888–894. - PubMed
-
- Tjendraputra E, Tran VH, Biu-Brennan D, Roufogalis BD, Duke CC. Effect of ginger constituents and synthetic analogues on cyclooxygenase-2 enzyme in intact cells. Bioorg. Chem. 2001;29:156–163. - PubMed
-
- Grzanna R, Lindmark L, Frondoza CG. Ginger—an herbal medicinal product with broad anti-inflammatory actions. J. Med. Food. 2005;8:125–132. - PubMed
-
- Kiuchi F, Iwakami S, Shibuya M, Hanaoka F, Sankawa U. Inhibition of prostaglandin and leukotriene biosynthesis by gingerols and diaryl heptanoids. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1992;40:387–391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

