The dopamine D(4) receptor, the ultimate disordered protein
- PMID: 20836733
- PMCID: PMC2953771
- DOI: 10.3109/10799893.2010.513842
The dopamine D(4) receptor, the ultimate disordered protein
Abstract
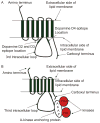
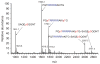
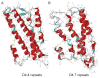
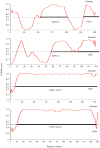
The human D4 dopamine receptor is a synaptic neurotransmitter receptor responsible for neuronal signaling in the mesolimbic system of the brain, an area of the brain that regulates emotion and complex behavior. Its structure makes it a very unusual and interesting G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) as it has several polymorphic variants of its gene in the region encoding the third intracellular loop (IL3). This region contains from two to seven or more similar 48 base pair repeats. These repeats cause this protein to have a very high disorder index and this, in turn, makes it very interactive with other proteins. Among GPCRs in general, the unusually proline-rich IL3 is unique to the D4 receptor (D4R). We believe that, as in the D2R, this region of the receptor plays a role in it's interaction with other receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, NIH. The authors thank the Office of National Drug Control Policy (ONDCP) for instrumentation funding, without which this and other projects could not have been accomplished.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional and pharmacological role of the dopamine D4 receptor and its polymorphic variants.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 30;13:1014678. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1014678. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36267569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopamine D4 receptor ubiquitination.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Apr 15;44(2):601-5. doi: 10.1042/BST20150281. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 27068976 Review.
-
Heteromerization between α2A adrenoceptors and different polymorphic variants of the dopamine D4 receptor determines pharmacological and functional differences. Implications for impulsive-control disorders.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Aug;170:105745. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105745. Epub 2021 Jun 26. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 34182128 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the Functional Role of Dopamine D4 Receptor Gene Polymorphisms: Heteromerization-Dependent Gain of Function of the D4.7 Receptor Variant.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Jul;56(7):4778-4785. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1413-1. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30387076 Free PMC article.
-
Role of dimerization in dopamine D(4) receptor biogenesis.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2014;15(7):659-65. doi: 10.2174/1389203715666140901110256. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2014. PMID: 25175456 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying NMDARs Dysfunction and Their Role in ADHD Pathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 19;24(16):12983. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612983. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histidine, the less interactive cousin of arginine.Eur J Mass Spectrom (Chichester). 2019 Apr;25(2):212-218. doi: 10.1177/1469066718791793. Eur J Mass Spectrom (Chichester). 2019. PMID: 31018697 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose tissue derived stromal cells in a gelatin-based 3D matrix with exclusive ascorbic acid signalling emerged as a novel neural tissue engineering construct: an innovative prototype for soft tissue.Regen Biomater. 2022 May 24;9:rbac031. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbac031. eCollection 2022. Regen Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35702348 Free PMC article.
-
Underlying Susceptibility to Eating Disorders and Drug Abuse: Genetic and Pharmacological Aspects of Dopamine D4 Receptors.Nutrients. 2020 Jul 30;12(8):2288. doi: 10.3390/nu12082288. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32751662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging of noncovalent complexes by MALDI-MS.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2013 Dec;24(12):1950-6. doi: 10.1007/s13361-013-0745-3. Epub 2013 Oct 2. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2013. PMID: 24092630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Missale C, Nash SR, Robinson SW, Jaber M, Caron MG. Dopamine receptors: from structure to function. Physiol Rev. 1998;78:189–225. - PubMed
-
- Aizman O, Brismar H, Uhlén P, Zettergren E, Levey AI, Forssberg H, Greengard P, Aperia A. Anatomical and physiological evidence for D1 and D2 dopamine receptor co-localization in neostriatal neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:226–230. - PubMed
-
- Van Tol HH, Wu CM, Guan HC, Ohara K, Bunzow JR, Civelli O, Kennedy J, Seeman P, Niznik HB, Jovanovic V. Multiple dopamine D4 receptor variants in the human population. Nature. 1992;358:149–152. - PubMed
-
- Oak JN, Oldenhof J, Van Tol HH. The dopamine D(4) receptor: one decade of research. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;405:303–327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
