Protective action of taurine, given as a pretreatment or as a posttreatment, against endotoxin-induced acute lung inflammation in hamsters
- PMID: 20804593
- PMCID: PMC2994390
- DOI: 10.1186/1423-0127-17-S1-S19
Protective action of taurine, given as a pretreatment or as a posttreatment, against endotoxin-induced acute lung inflammation in hamsters
Abstract
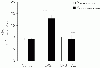
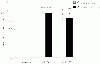
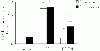
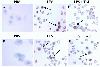
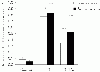
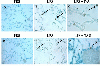
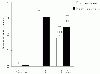
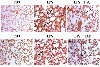
To assess the effect of taurine on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced lung inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis, female Golden Syrian hamsters were intratracheally instilled with bacterial LPS (0.02 mg in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4), before or after a 3-day intraperitoneal treatment with a single dose of taurine (50 mg/kg/day in PBS pH 7.4), and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and lung tissue samples were collected at 24 hr after the last treatment. In comparison to BALF samples from animals receiving only PBS pH 7.4, and serving as controls, those of LPS-stimulated animals exhibited a higher count of both total leukocytes and neutrophils and increased expression of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1. In comparison to lungs from control animals, those from LPS-treated animals showed increased cellular apoptosis, lipid peroxidation, decreased glutathione levels, altered activities of antioxidant enzymes (catalase, glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase) and focal inflammation confined to the parenchyma. A treatment with taurine was found to significantly attenuate all these alterations, with the protection being, in all instances, greater when given before rather than after LPS. The present results suggest that taurine is endowed with antiinflammatory and antioxidant properties that are protective in the lung against the deleterious actions of Gram negative bacterial endotoxin.
Figures
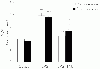
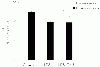
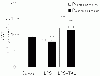
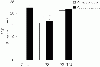
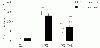
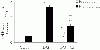

Similar articles
-
Attenuating effect of taurine on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in hamsters.Pharmacol Res. 2009 Nov;60(5):418-28. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2009.05.006. Epub 2009 May 23. Pharmacol Res. 2009. PMID: 19467329
-
Effect of betulinic acid on neutrophil recruitment and inflammatory mediator expression in lipopolysaccharide-induced lung inflammation in rats.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2012 May 12;46(1-2):106-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2012.02.015. Epub 2012 Mar 3. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2012. PMID: 22402186
-
The protective effect of Nigella sativa extract on lung inflammation and oxidative stress induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 May 10;253:112653. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112653. Epub 2020 Feb 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32035219
-
Protective role of taurine against oxidative stress (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2021 Aug;24(2):605. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12242. Epub 2021 Jun 29. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34184084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taurine and Its Anticancer Functions: In Vivo and In Vitro Study.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1370:121-128. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-93337-1_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35882787 Review.
Cited by
-
A systematic review of preclinical studies on the efficacy of taurine for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Amino Acids. 2021 Jun;53(6):783-800. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-02988-8. Epub 2021 Apr 30. Amino Acids. 2021. PMID: 33929638
-
The effect of taurine on the relationship between NO, ADMA and homocysteine in endotoxin-mediated inflammation in HUVEC cultures.Inflammation. 2014 Oct;37(5):1439-43. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-9868-3. Inflammation. 2014. PMID: 24604342
-
Effects of S-allyl cysteine on lung and liver tissue in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015 Mar;388(3):327-35. doi: 10.1007/s00210-014-1076-z. Epub 2014 Dec 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25480742
-
Nutraceutical Strategies for Suppressing NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation: Pertinence to the Management of COVID-19 and Beyond.Nutrients. 2020 Dec 25;13(1):47. doi: 10.3390/nu13010047. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33375692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Sequencing and Related Differential Gene Expression Analysis in a Mouse Model of Emphysema Induced by Tobacco Smoke Combined with Elastin Peptides.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023 Oct 3;18:2147-2161. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S397400. eCollection 2023. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023. PMID: 37810372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chignard M, Balloy V. Neutrophil recruitment and increased permeability during acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2000;279:L1083–L1090. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

