Modulation of GEF-H1 induced signaling by heparanase in brain metastatic melanoma cells
- PMID: 20803552
- PMCID: PMC3007595
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.22854
Modulation of GEF-H1 induced signaling by heparanase in brain metastatic melanoma cells
Abstract
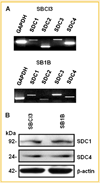
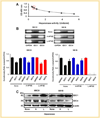
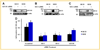
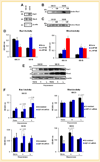
Mechanisms of brain metastatic melanoma (BMM) remain largely unknown. Understanding the modulation of signaling pathways that alter BMM cell invasion and metastasis is critical to develop new therapies for BMM. Heparanase has been widely implicated in cancer and is the dominant mammalian endoglycosidase which degrades heparan sulfate chains of proteoglycans (HSPG) including syndecans (SDCs). Recent findings also indicate that heparanase possesses non-enzymatic functions in its latent form. We hypothesized that extracellular heparanase modulates BMM cell signaling by involving SDC1/4 carboxy terminal-associated proteins and downstream targets. We digested BMM cell surface HS with human recombinant active or latent heparanase to delineate their effects on cytoskeletal dynamics and cell invasiveness. We identified the small GTPase guanine nucleotide exchange factor-H1 (GEF-H1) as a new component of a SDC signaling complex that is differentially expressed in BMM cells compared to corresponding non-metastatic counterparts. Second, knockdown of GEF-H1, SDC1, or SDC4 decreased BMM cell invasiveness and GEF-H1 modulated small GTPase activity of Rac1 and RhoA in conjunction with heparanase treatment. Third, both active and latent forms of heparanase affected Rac1 and RhoA activity; notably increasing RhoA activity. Both forms of heparanase were found to mediate the expression and subcellular localization of GEF-H1, and treatment of BMM with latent heparanase modulated SDC1/4 gene expression. Finally, treatment with exogenous heparanase downregulated BMM cell invasion. These studies indicate the relevance of heparanase signaling pathways in BMM progression, and provide insights into the molecular mechanisms regulating HSPG signaling in response to exogenous heparanase.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Heparanase-induced GEF-H1 signaling regulates the cytoskeletal dynamics of brain metastatic breast cancer cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2012 Jun;10(6):689-702. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0534. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Mol Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22513363 Free PMC article.
-
Heparanase Modulates Shh and Wnt3a Signaling in Human Medulloblastoma Cells.Exp Ther Med. 2011 Mar 1;2(2):229-238. doi: 10.3892/etm.2010.189. Exp Ther Med. 2011. PMID: 21442027 Free PMC article.
-
Heparanase degrades syndecan-1 and perlecan heparan sulfate: functional implications for tumor cell invasion.J Biol Chem. 2004 Feb 27;279(9):8047-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304872200. Epub 2003 Nov 20. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14630925
-
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Tiam1: a Janus-faced molecule in cellular signaling.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):483-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.034. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24308970 Review.
-
Proteoglycans in health and disease: new concepts for heparanase function in tumor progression and metastasis.FEBS J. 2010 Oct;277(19):3890-903. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07799.x. Epub 2010 Aug 31. FEBS J. 2010. PMID: 20840586 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Guanine nucleotide exchange factor H1 can be a new biomarker of melanoma.Biologics. 2016 Jul 5;10:89-98. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S109643. eCollection 2016. Biologics. 2016. PMID: 27462139 Free PMC article.
-
Rho GTPases in the Amygdala-A Switch for Fears?Cells. 2020 Aug 26;9(9):1972. doi: 10.3390/cells9091972. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32858950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Androgen deprivation restores ARHGEF2 to promote neuroendocrine differentiation of prostate cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Nov 5;13(11):927. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05366-8. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36335093 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the blood-brain barrier in the formation of brain metastases.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jan 11;14(1):1383-411. doi: 10.3390/ijms14011383. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23344048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation Imputation for Single-Cell RNA-seq.J Comput Biol. 2022 May;29(5):465-482. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2021.0403. Epub 2022 Mar 21. J Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 35325552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander CM, Reichsman F, Hinkes MT, Lincecum J, Becker KA, Cumberledge S, Bernfield M. Syndecan-1 is required for Wnt-1-induced mammary tumorigenesis in mice. Nat Genet. 2000;25:329–332. - PubMed
-
- Avalos AM, Valdivia AD, Munoz N, Herrera-Molina R, Tapia JC, Lavandero S, Chiong M, Burridge K, Schneider P, Quest AF, Leyton L. Neuronal Thy-1 induces astrocyte adhesion by engaging syndecan-4 in a cooperative interaction with alphavbeta3 integrin that activates PKCalpha and RhoA. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:3462–3471. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beauvais DM, Rapraeger AC. Syndecan-1-mediated cell spreading requires signaling by alphavbeta3 integrins in human breast carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 2003;286:219–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

