The role of fibroblast Tiam1 in tumor cell invasion and metastasis
- PMID: 20802514
- PMCID: PMC2997941
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.385
The role of fibroblast Tiam1 in tumor cell invasion and metastasis
Abstract
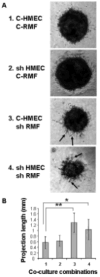
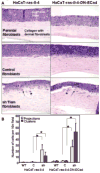
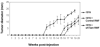
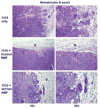
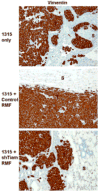
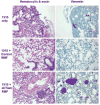
The co-evolution of tumors and their microenvironment involves bidirectional communication between tumor cells and tumor-associated stroma. Various cell types are present in tumor-associated stroma, of which fibroblasts are the most abundant. The Rac exchange factor Tiam1 is implicated in multiple signaling pathways in epithelial tumor cells and lack of Tiam1 in tumor cells retards tumor growth in Tiam1 knockout mouse models. Conversely, tumors arising in Tiam1 knockout mice have increased invasiveness. We have investigated the role of Tiam1 in tumor-associated fibroblasts as a modulator of tumor cell invasion and metastasis, using retroviral delivery of short hairpin RNA to suppress Tiam1 levels in three different experimental models. In spheroid co-culture of mammary epithelial cells and fibroblasts, Tiam1 silencing in fibroblasts led to increased epithelial cell outgrowth into matrix. In tissue-engineered human skin, Tiam1 silencing in dermal fibroblasts led to increased invasiveness of epidermal keratinocytes with pre-malignant features. In a model of human breast cancer in mice, co-implantation of mammary fibroblasts inhibited tumor invasion and metastasis, which was reversed by Tiam1 silencing in co-injected fibroblasts. These results suggest that stromal Tiam1 may have a role in modulating the effects of the tumor microenvironment on malignant cell invasion and metastasis. This suggests a set of pathways for further investigation, with implications for future therapeutic targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tiam1-regulated osteopontin in senescent fibroblasts contributes to the migration and invasion of associated epithelial cells.J Cell Sci. 2012 Jan 15;125(Pt 2):376-86. doi: 10.1242/jcs.089466. Epub 2012 Feb 2. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22302986 Free PMC article.
-
The fibroblast Tiam1-osteopontin pathway modulates breast cancer invasion and metastasis.Breast Cancer Res. 2016 Jan 28;18(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0674-8. Breast Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26821678 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of breast cancer cell motility by T-cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis-inducing protein.Breast Cancer Res. 2010;12(5):R69. doi: 10.1186/bcr2637. Epub 2010 Sep 6. Breast Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20819206 Free PMC article.
-
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Tiam1: a Janus-faced molecule in cellular signaling.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):483-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.034. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24308970 Review.
-
The role of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor Tiam1 in cellular migration, invasion, adhesion and tumor progression.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004 Mar;84(1):21-32. doi: 10.1023/B:BREA.0000018421.31632.e6. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004. PMID: 14999151 Review.
Cited by
-
High Tiam1 expression predicts positive lymphatic metastasis and worse survival in patients with malignant solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Jul 25;12:5925-5936. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S191571. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31413590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNAi mediated Tiam1 gene knockdown inhibits invasion of retinoblastoma.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 7;8(8):e70422. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070422. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23950931 Free PMC article.
-
Tiam1-regulated osteopontin in senescent fibroblasts contributes to the migration and invasion of associated epithelial cells.J Cell Sci. 2012 Jan 15;125(Pt 2):376-86. doi: 10.1242/jcs.089466. Epub 2012 Feb 2. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22302986 Free PMC article.
-
Can't handle the stress? Mechanobiology and disease.Trends Mol Med. 2022 Sep;28(9):710-725. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2022.05.010. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Trends Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35717527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of Agelastatin Derivatives as Potent Modulators for Cancer Invasion and Metastasis.J Org Chem. 2017 Aug 4;82(15):7720-7731. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.7b01162. Epub 2017 Jul 25. J Org Chem. 2017. PMID: 28696693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andriani F, Garfield J, Fusenig NE, Garlick JA. Int J Cancer. 2004;108:348–57. - PubMed
-
- Baines AT, Lim KH, Shields JM, Lambert JM, Counter CM, Der CJ, Cox AD. Methods Enzymol. 2006;407:556–74. - PubMed
-
- Bhowmick NA, Chytil A, Plieth D, Gorska AE, Dumont N, Shappell S, Washington MK, Neilson EG, Moses HL. Science. 2004a;303:848–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

