Strand-specific RNA sequencing reveals extensive regulated long antisense transcripts that are conserved across yeast species
- PMID: 20796282
- PMCID: PMC2945789
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-8-r87
Strand-specific RNA sequencing reveals extensive regulated long antisense transcripts that are conserved across yeast species
Abstract
Background: Recent studies in budding yeast have shown that antisense transcription occurs at many loci. However, the functional role of antisense transcripts has been demonstrated only in a few cases and it has been suggested that most antisense transcripts may result from promiscuous bi-directional transcription in a dense genome.
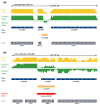
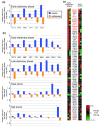
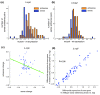
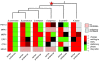
Results: Here, we use strand-specific RNA sequencing to study anti-sense transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We detect 1,103 putative antisense transcripts expressed in mid-log phase growth, ranging from 39 short transcripts covering only the 3' UTR of sense genes to 145 long transcripts covering the entire sense open reading frame. Many of these antisense transcripts overlap sense genes that are repressed in mid-log phase and are important in stationary phase, stress response, or meiosis. We validate the differential regulation of 67 antisense transcripts and their sense targets in relevant conditions, including nutrient limitation and environmental stresses. Moreover, we show that several antisense transcripts and, in some cases, their differential expression have been conserved across five species of yeast spanning 150 million years of evolution. Divergence in the regulation of antisense transcripts to two respiratory genes coincides with the evolution of respiro-fermentation.
Conclusions: Our work provides support for a global and conserved role for antisense transcription in yeast gene regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Examining the condition-specific antisense transcription in S. cerevisiae and S. paradoxus.BMC Genomics. 2014 Jun 25;15(1):521. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-521. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24965678 Free PMC article.
-
Pervasive antisense transcription is evolutionarily conserved in budding yeast.Mol Biol Evol. 2013 Feb;30(2):409-21. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mss240. Epub 2012 Oct 18. Mol Biol Evol. 2013. PMID: 23079418
-
A conserved regulatory role for antisense RNA in meiotic gene expression in yeast.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2011 Dec;14(6):655-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2011.09.010. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21963111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Native elongating transcript sequencing reveals global anti-correlation between sense and antisense nascent transcription in fission yeast.RNA. 2018 Feb;24(2):196-208. doi: 10.1261/rna.063446.117. Epub 2017 Nov 7. RNA. 2018. PMID: 29114019 Free PMC article.
-
Antisense gene expression in yeast.Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1994 Nov;375(11):721-9. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1994.375.11.721. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1994. PMID: 7695834 Review.
Cited by
-
Zinc-dependent regulation of the Adh1 antisense transcript in fission yeast.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 11;288(2):759-69. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.406165. Epub 2012 Dec 5. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23223230 Free PMC article.
-
Extracting novel hypotheses and findings from RNA-seq data.FEMS Yeast Res. 2020 Mar 1;20(2):foaa007. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/foaa007. FEMS Yeast Res. 2020. PMID: 32009158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
XUTs are a class of Xrn1-sensitive antisense regulatory non-coding RNA in yeast.Nature. 2011 Jun 22;475(7354):114-7. doi: 10.1038/nature10118. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21697827
-
Natural antisense transcripts as versatile regulators of gene expression.Nat Rev Genet. 2024 Oct;25(10):730-744. doi: 10.1038/s41576-024-00723-z. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Nat Rev Genet. 2024. PMID: 38632496 Review.
-
Competition between pre-mRNAs for the splicing machinery drives global regulation of splicing.Mol Cell. 2013 Aug 8;51(3):338-48. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.06.012. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23891561 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

