Interaction of serum- and glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) with the WW-domains of Nedd4-2 is required for epithelial sodium channel regulation
- PMID: 20730100
- PMCID: PMC2921341
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012163
Interaction of serum- and glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) with the WW-domains of Nedd4-2 is required for epithelial sodium channel regulation
Abstract
Background: The epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) is an integral component of the pathway for Na(+) absorption in epithelial cells. The ubiquitin ligases Nedd4 and Nedd4-2 bind to ENaC and decrease its activity. Conversely, Serum- and Glucocorticoid regulated Kinase-1 (SGK1), a downstream mediator of aldosterone, increases ENaC activity. This effect is at least partly mediated by direct interaction between SGK and Nedd4-2. SGK binds both Nedd4 and Nedd4-2, but it is only able to phosphorylate Nedd4-2. Phosphorylation of Nedd4-2 reduces its ability to bind to ENaC, due to the interaction of phosphorylated Nedd4-2 with 14-3-3 proteins, and hence increases ENaC activity. WW-domains in Nedd4-like proteins bind PY-motifs (PPXY) present in ENaC subunits, and SGK also has a PY-motif.
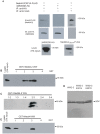
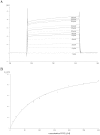
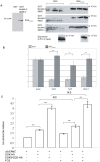
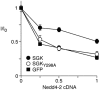
Principal finding: Here we show that single or tandem WW-domains of Nedd4 and Nedd4-2 mediate binding to SGK and that different WW-domains of Nedd4 and Nedd4-2 are involved. Our data also show that WW-domains 2 and 3 of Nedd4-2 mediate the interaction with SGK in a cooperative manner, that activated SGK has increased affinity for the WW-domains of Nedd4-2 in vitro, and a greater stimulatory effect on ENaC Na(+) transport compared to wildtype SGK. Further, SGK lacking a PY motif failed to stimulate ENaC activity in the presence of Nedd4-2.
Conclusions: Binding of Nedd4-2 WW-domains to SGK is necessary for SGK-induced ENaC activity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stimulation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) by the serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase (Sgk) involves the PY motifs of the channel but is independent of sodium feedback inhibition.Pflugers Arch. 2006 Jun;452(3):290-9. doi: 10.1007/s00424-005-0026-5. Epub 2006 Jan 17. Pflugers Arch. 2006. PMID: 16416336
-
Serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase modulates Nedd4-2-mediated inhibition of the epithelial Na+ channel.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jan 4;277(1):5-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C100623200. Epub 2001 Nov 5. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11696533
-
cAMP and serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase (SGK) regulate the epithelial Na(+) channel through convergent phosphorylation of Nedd4-2.J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 29;279(44):45753-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407858200. Epub 2004 Aug 24. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15328345
-
Regulation of epithelial Na+ channels by aldosterone: role of Sgk1.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2008 Feb;35(2):235-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2007.04844.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18197893 Review.
-
Regulation of the epithelial Na+ channel by Nedd4 and ubiquitination.Kidney Int. 2000 Mar;57(3):809-15. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00919.x. Kidney Int. 2000. PMID: 10720933 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin ameliorates pulmonary edema through the upregulation of epithelial sodium channel via the PI3K/SGK1 pathway in mice with lipopolysaccharide‑induced lung injury.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Mar;19(3):1665-1677. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.9809. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 30628684 Free PMC article.
-
Orai3 calcium channel and resistance to chemotherapy in breast cancer cells: the p53 connection.Cell Death Differ. 2018 Mar;25(4):693-707. doi: 10.1038/s41418-017-0007-1. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Cell Death Differ. 2018. PMID: 29323264 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of immune responses by mTOR.Annu Rev Immunol. 2012;30:39-68. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075024. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Annu Rev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22136167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucocorticoids and serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 are potent regulators of CFTR in the native intestine: implications for stress-induced diarrhea.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020 Aug 1;319(2):G121-G132. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00076.2020. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32567324 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Plasma Membrane Lipid Composition in Hypertensive Neutrophils Impacts Epithelial Sodium Channel (ENaC) Endocytosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 30;25(9):4939. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094939. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garty H, Palmer LG. Epithelial sodium channels: function, structure, and regulation. Physiol Rev. 1997;77:359–396. - PubMed
-
- Snyder PM, Steines JC, Olson DR. Relative contribution of Nedd4 and Nedd4-2 to ENaC regulation in epithelia determined by RNA interference. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:5042–5046. - PubMed
-
- Snyder PM. Minireview: regulation of epithelial Na+ channel trafficking. Endocrinology. 2005;146:5079–5085. - PubMed
-
- Hughey RP, Bruns JB, Kinlough CL, Harkleroad KL, Tong Q, et al. Epithelial sodium channels are activated by furin-dependent proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:18111–18114. - PubMed
-
- Bruns JB, Carattino MD, Sheng S, Maarouf AB, Weisz OA, et al. Epithelial Na+ channels are fully activated by furin- and prostasin-dependent release of an inhibitory peptide from the gamma-subunit. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:6153–6160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

