beta1-integrin is dispensable for the induction of ErbB2 mammary tumors but plays a critical role in the metastatic phase of tumor progression
- PMID: 20713705
- PMCID: PMC2932605
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1003034107
beta1-integrin is dispensable for the induction of ErbB2 mammary tumors but plays a critical role in the metastatic phase of tumor progression
Abstract
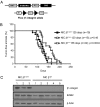
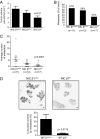
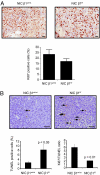
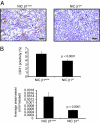
Cross-talk between integrin receptors and activated growth factor receptors has been hypothesized to play a critical role in the initiation and progression of cancer. Despite in vitro evidence documenting the important role of integrin receptors in the regulation of cancer cell proliferation, the relative contribution of the integrin receptors to the initiation and progression of tumors remains unclear. Previous studies with a polyomavirus middle T mammary tumor model have indicated that targeted disruption of beta1-integrin in the mammary glands of these mice completely blocks tumor induction. To further explore the general significance of these observations, we have crossed these conditional beta1-integrin strains to a strain of mice carrying mouse mammary tumor virus/activated erbB2 (herein referred to as the NIC strain). In contrast to the tumor induction block in the polyomavirus middle T model, tumor onset in the beta1-integrin-deficient NIC mice was delayed by only 30 d and was 100% penetrant. This modest effect on tumor induction was not a result of inefficient excision, as all tumors were confirmed as beta1-integrin-null. Animals bearing beta1-integrin-deficient ErbB2 tumors exhibited significantly reduced tumor volume, which was associated with increased tumor cell apoptosis and a reduction in tumor angiogenesis. In addition, beta1-integrin-deficient tumors were compromised in their capacity to metastasize to the lung, a deficiency associated with abrogation of adhesion signaling. Taken together, these observations suggest that, although beta1-integrin is dispensable for the initiation of ErbB2 tumor induction, it plays a critical role in metastatic phase of tumor progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Focal adhesion kinase contributes to proliferative potential of ErbB2 mammary tumour cells but is dispensable for ErbB2 mammary tumour induction in vivo.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Feb 28;14(1):R36. doi: 10.1186/bcr3131. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22373082 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin deficiency limits tumor vascularization in the MMTV-PyV-mT mouse model of mammary cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 May 15;15(10):3256-64. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2661. Epub 2009 May 15. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19447866 Free PMC article.
-
The glucose transporter GLUT1 is required for ErbB2-induced mammary tumorigenesis.Breast Cancer Res. 2016 Dec 20;18(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0795-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27998284 Free PMC article.
-
β1-integrins signaling and mammary tumor progression in transgenic mouse models: implications for human breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13(6):229. doi: 10.1186/bcr2905. Epub 2011 Nov 30. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22264244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developmental timing of activated erbB2 expression plays a critical role in the induction of mammary tumors.Cell Cycle. 2004 Sep;3(9):1111-3. Epub 2004 Sep 1. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 15326381 Review.
Cited by
-
A cell-ECM screening method to predict breast cancer metastasis.Integr Biol (Camb). 2015 Feb;7(2):198-212. doi: 10.1039/c4ib00218k. Integr Biol (Camb). 2015. PMID: 25537447 Free PMC article.
-
Focal adhesion kinase contributes to proliferative potential of ErbB2 mammary tumour cells but is dispensable for ErbB2 mammary tumour induction in vivo.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Feb 28;14(1):R36. doi: 10.1186/bcr3131. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22373082 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Therapeutic Efficacy of Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus-1 with Integrin β1 Blocking Antibody OS2966.Mol Cancer Ther. 2019 Jun;18(6):1127-1136. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0953. Epub 2019 Mar 29. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 30926634 Free PMC article.
-
When Good Turns Bad: Regulation of Invasion and Metastasis by ErbB2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase.Cells. 2014 Jan 27;3(1):53-78. doi: 10.3390/cells3010053. Cells. 2014. PMID: 24709902 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage response genes and the development of cancer metastasis.Radiat Res. 2014 Feb;181(2):111-30. doi: 10.1667/RR13515.1. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Radiat Res. 2014. PMID: 24397478 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Grasso AW, et al. ErbB kinases and NDF signaling in human prostate cancer cells. Oncogene. 1997;15:2705–2716. - PubMed
-
- Guo W, et al. Beta 4 integrin amplifies ErbB2 signaling to promote mammary tumorigenesis. Cell. 2006;126:489–502. - PubMed
-
- White DE, et al. Targeted disruption of beta1-integrin in a transgenic mouse model of human breast cancer reveals an essential role in mammary tumor induction. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:159–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

