Phosphorylation and activation of androgen receptor by Aurora-A
- PMID: 20713353
- PMCID: PMC2963369
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.121129
Phosphorylation and activation of androgen receptor by Aurora-A
Retraction in
-
Phosphorylation and activation of androgen receptor by Aurora-A.J Biol Chem. 2016 Oct 21;291(43):22854. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A110.121129. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27825092 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
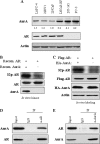
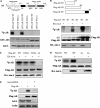
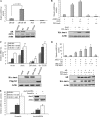
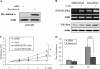
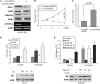
Aurora-A kinase is frequently overexpressed/activated in various types of human malignancy, including prostate cancer. In this study, we demonstrate elevated levels of Aurora-A in androgen-refractory LNCaP-RF but not androgen-sensitive LNCaP cells, which prompted us to examine whether Aurora-A regulates the androgen receptor (AR) and whether elevated Aurora-A is involved in androgen-independent cell growth. We show that ectopic expression of Aurora-A induces AR transactivation activity in the presence and absence of androgen. Aurora-A interacts with AR and phosphorylates AR at Thr(282) and Ser(293) in vitro and in vivo. Aurora-A induces AR transactivation activity in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. Ectopic expression of Aurora-A in LNCaP cells induces prostate-specific antigen expression and cell survival, whereas knockdown of Aurora-A sensitizes LNCaP-RF cells to apoptosis and cell growth arrest. These data indicate that AR is a substrate of Aurora-A and that elevated Aurora-A could contribute to androgen-independent cell growth by phosphorylation and activation of AR.
Figures
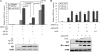

Similar articles
-
TGF-beta signaling and androgen receptor status determine apoptotic cross-talk in human prostate cancer cells.Prostate. 2008 Feb 15;68(3):287-95. doi: 10.1002/pros.20698. Prostate. 2008. PMID: 18163430
-
Soluble factors derived from stroma activated androgen receptor phosphorylation in human prostate LNCaP cells: roles of ERK/MAP kinase.Prostate. 2009 Jun 15;69(9):949-55. doi: 10.1002/pros.20944. Prostate. 2009. PMID: 19274665 Free PMC article.
-
Activated Cdc42-associated kinase Ack1 promotes prostate cancer progression via androgen receptor tyrosine phosphorylation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 May 15;104(20):8438-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700420104. Epub 2007 May 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17494760 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of HSP90 by protein kinase A is essential for the nuclear translocation of androgen receptor.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 31;294(22):8699-8710. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007420. Epub 2019 Apr 16. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30992362 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction pathways in androgen-dependent and -independent prostate cancer cell proliferation.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005 Mar;12(1):119-34. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.00835. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15788644
Cited by
-
Calmodulin activation of Aurora-A kinase (AURKA) is required during ciliary disassembly and in mitosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Jul;23(14):2658-70. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-12-1056. Epub 2012 May 23. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22621899 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer development and progression.J Carcinog. 2011;10:20. doi: 10.4103/1477-3163.83937. Epub 2011 Aug 23. J Carcinog. 2011. PMID: 21886458 Free PMC article.
-
Minireview: Alternative activation pathways for the androgen receptor in prostate cancer.Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Jun;25(6):897-907. doi: 10.1210/me.2010-0469. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Mol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21436259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aurora A regulates expression of AR-V7 in models of castrate resistant prostate cancer.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 16;7:40957. doi: 10.1038/srep40957. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28205582 Free PMC article.
-
The role of intracrine androgen metabolism, androgen receptor and apoptosis in the survival and recurrence of prostate cancer during androgen deprivation therapy.Curr Drug Targets. 2013 Apr;14(4):420-40. doi: 10.2174/1389450111314040004. Curr Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 23565755 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Heinlein C. A., Chang C. (2004) Endocr. Rev. 25, 276–308 - PubMed
-
- Wang Q., Li W., Zhang Y., Yuan X., Xu K., Yu J., Chen Z., Beroukhim R., Wang H., Lupien M., Wu T., Regan M. M., Meyer C. A., Carroll J. S., Manrai A. K., Jänne O. A., Balk S. P., Mehra R., Han B., Chinnaiyan A. M., Rubin M. A., True L., Fiorentino M., Fiore C., Loda M., Kantoff P. W., Liu X. S., Brown M. (2009) Cell 138, 245–256 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen C. D., Welsbie D. S., Tran C., Baek S. H., Chen R., Vessella R., Rosenfeld M. G., Sawyers C. L. (2004) Nat. Med. 10, 33–39 - PubMed
-
- Taplin M. E., Bubley G. J., Shuster T. D., Frantz M. E., Spooner A. E., Ogata G. K., Keer H. N., Balk S. P. (1995) N. Engl. J. Med. 332, 1393–1398 - PubMed
-
- Culig Z. (2004) Growth Factors 22, 179–184 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

