Peptidic HIV integrase inhibitors derived from HIV gene products: structure-activity relationship studies
- PMID: 20708407
- PMCID: PMC4486254
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2010.07.050
Peptidic HIV integrase inhibitors derived from HIV gene products: structure-activity relationship studies
Abstract
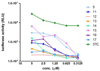
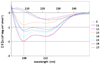
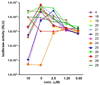
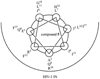
Structure-activity relationship studies were conducted on HIV integrase (IN) inhibitory peptides which were found by the screening of an overlapping peptide library derived from HIV-1 gene products. Since these peptides located in the second helix of Vpr are considered to have an alpha-helical conformation, Glu-Lys pairs were introduced into the i and i+4 positions to increase the helicity of the lead compound possessing an octa-arginyl group. Ala-scan was also performed on the lead compound for the identification of the amino acid residues responsible for the inhibitory activity. The results indicated the importance of an alpha-helical structure for the expression of inhibitory activity, and presented a binding model of integrase and the lead compound.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cell-permeable stapled peptides based on HIV-1 integrase inhibitors derived from HIV-1 gene products.ACS Chem Biol. 2013 Oct 18;8(10):2235-44. doi: 10.1021/cb400495h. Epub 2013 Aug 15. ACS Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23898787 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide HIV-1 integrase inhibitors from HIV-1 gene products.J Med Chem. 2010 Jul 22;53(14):5356-60. doi: 10.1021/jm1003528. J Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20586421 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the activities of reverse transcriptase and integrase of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 by peptides derived from the homologous viral protein R (Vpr).J Mol Biol. 2007 Jun 22;369(5):1230-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.03.073. Epub 2007 Apr 1. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17490682
-
Structure-activity relationships of HIV-1 integrase inhibitors--enzyme-ligand interactions.Curr Med Chem. 2003 Sep;10(18):1795-810. doi: 10.2174/0929867033456981. Curr Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 12871105 Review.
-
Peptides as new inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and integrase.Curr Med Chem. 2003 Sep;10(18):1765-78. doi: 10.2174/0929867033457007. Curr Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 12871103 Review.
Cited by
-
Small-Molecule Anti-HIV-1 Agents Based on HIV-1 Capsid Proteins.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 3;11(2):208. doi: 10.3390/biom11020208. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33546092 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-permeable stapled peptides based on HIV-1 integrase inhibitors derived from HIV-1 gene products.ACS Chem Biol. 2013 Oct 18;8(10):2235-44. doi: 10.1021/cb400495h. Epub 2013 Aug 15. ACS Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23898787 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting the HIV integration process: past, present, and the future.J Med Chem. 2014 Feb 13;57(3):539-66. doi: 10.1021/jm400674a. Epub 2013 Sep 25. J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24025027 Free PMC article.
-
HIV integrase inhibitors: 20-year landmark and challenges.Adv Pharmacol. 2013;67:75-105. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-405880-4.00003-2. Adv Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23885999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of peptide inhibitors of HIV transmission.Bioact Mater. 2016 Sep 16;1(2):109-121. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2016.09.004. eCollection 2016 Dec. Bioact Mater. 2016. PMID: 29744399 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mitsuya H, Erickson J. In: Textbook of AIDS Medicine. Merigan TC, Bartlett JG, Bolognesi D, editors. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins; 1999. pp. 751–780.
-
- Farnet CM, Bushman FD. Cell. 1997;88:483. - PubMed
- Chen H, Engelman A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1998;95:15270. - PMC - PubMed
- Gleenberg IO, Herschhorn A, Hizi A. J. Mol. Biol. 2007;369:1230. - PubMed
- Gleenberg IO, Avidan O, Goldgur Y, Herschhorn A, Hizi A. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:21987. - PubMed
- Hehl EA, Joshi P, Kalpana GV, Prasad VR. J. Virol. 2004;78:5056. - PMC - PubMed
- Tasara T, Maga G, Hottiger MO, Hubscher U. FEBS Lett. 2001;507:39. - PubMed
- Gleenberg IO, Herschhorn A, Goldgur Y, Hizi A. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007;458:202. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki T, Futaki S, Niwa M, Tanaka S, Ueda K, Sugiura Y. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:2437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information

