Effects of PCSK9 genetic variants on plasma LDL cholesterol levels and risk of premature myocardial infarction in the Italian population
- PMID: 20699424
- PMCID: PMC2952575
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M010009
Effects of PCSK9 genetic variants on plasma LDL cholesterol levels and risk of premature myocardial infarction in the Italian population
Abstract
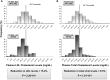
The R46L variant in the proprotein-convertase subtilisin-kexin type 9 (PCSK9) gene was associated with reduced levels of LDL and total cholesterol and with a lower risk of coronary artery disease. We investigated the association of R46L with myocardial infarction (MI) in 1,880 Italian patients with premature MI and 1,880 controls. A trend toward a protective effect of the L46 allele was observed [odds ratio (OR) = 0.75, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.49-1.13; P = 0.17], although the association with MI was not significant. This is probably due to the combined effect of the low frequency of R46L among Italians and of the young age of the analyzed cohort for whom the impact of coronary atherosclerosis is less important. This hypothesis was indirectly confirmed by the significant association found after including 1,056 additional older controls (OR = 0.67, 95% CI = 0.46-0.97; P = 0.036). LDL cholesterol was significantly lower in L46 carriers (116.2 ± 34.7 mg/dl) than in noncarriers (137.4 ± 47.3 mg/dl; P = 0.00022); a similar reduction was observed for total cholesterol (191.7 ± 37.7 vs. 211.7 ± 49 mg/dl; P = 0.00019). Analysis of 23 additional polymorphisms in the PCSK9 region identified another single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) (rs11206510) associated with cholesterol levels. We confirmed that the L46 allele not only decreases LDL cholesterol but also protects against MI. Moreover, we replicated the association of total and LDL cholesterol with the SNP rs11206510.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PCSK9 R46L Loss-of-Function Mutation Reduces Lipoprotein(a), LDL Cholesterol, and Risk of Aortic Valve Stenosis.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Sep;101(9):3281-7. doi: 10.1210/jc.2016-1206. Epub 2016 May 24. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27218270 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of protein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) 46L gene polymorphism on LDL cholesterol concentration in a Polish adult population.Mol Genet Metab. 2008 Jun;94(2):259-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2008.02.003. Epub 2008 Mar 14. Mol Genet Metab. 2008. PMID: 18343176
-
Relation of PCSK9 mutations to serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in childhood and adulthood (from The Bogalusa Heart Study).Am J Cardiol. 2007 Jul 1;100(1):69-72. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.02.057. Epub 2007 May 11. Am J Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 17599443 Clinical Trial.
-
PCSK9 R46L, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, and risk of ischemic heart disease: 3 independent studies and meta-analyses.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010 Jun 22;55(25):2833-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.02.044. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20579540 Review.
-
PCSK9 gene mutations and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.Clin Chim Acta. 2014 Apr 20;431:148-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2014.01.043. Epub 2014 Feb 8. Clin Chim Acta. 2014. PMID: 24518357 Review.
Cited by
-
Using Human 'Experiments of Nature' to Predict Drug Safety Issues: An Example with PCSK9 Inhibitors.Drug Saf. 2018 Mar;41(3):303-311. doi: 10.1007/s40264-017-0616-0. Drug Saf. 2018. PMID: 29185237 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships between genetic polymorphisms of E670G in PCSK9 gene and coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Aug 15;8(8):13251-8. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26550250 Free PMC article.
-
Pcsk9 is associated with severity of coronary artery lesions in male patients with premature myocardial infarction.Lipids Health Dis. 2021 May 27;20(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12944-021-01478-w. Lipids Health Dis. 2021. PMID: 34044829 Free PMC article.
-
Living the PCSK9 adventure: from the identification of a new gene in familial hypercholesterolemia towards a potential new class of anticholesterol drugs.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2014 Sep;16(9):439. doi: 10.1007/s11883-014-0439-8. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2014. PMID: 25052769 Review.
-
Molecular and cellular function of the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9).Basic Res Cardiol. 2015 Mar;110(2):4. doi: 10.1007/s00395-015-0463-z. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Basic Res Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25600226 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kuulasmaa K., Tunstall-Pedoe H., Dobson A., Fortmann S., Sans S., Tolonen H., Evans A., Ferrario M., Tuomilehto J. 2000. Estimation of contribution of changes in classic risk factors to trends in coronary-event rates across the WHO MONICA Project populations. Lancet. 355: 675–687. - PubMed
-
- Clarke R., Emberson J. R., Parish S., Palmer A., Shipley M., Linksted P., Sherliker P., Clark S., Armitage J., Fletcher A., et al. 2007. Cholesterol fractions and apolipoproteins as risk factors for heart disease mortality in older men. Arch. Intern. Med. 167: 1373–1378. - PubMed
-
- Lewington S., Whitlock G., Clarke R., Sherliker P., Emberson J., Halsey J., Qizilbash N., Peto R., Collins R. 2007. Blood cholesterol and vascular mortality by age, sex, and blood pressure: a meta-analysis of individual data from 61 prospective studies with 55,000 vascular deaths. Lancet. 370: 1829–1839. - PubMed
-
- Pollin T. I., Hsueh W. C., Steinle N. I., Snitker S., Shuldiner A. R., Mitchell B. D. 2004. A genome-wide scan of serum lipid levels in the Old Order Amish. Atherosclerosis. 173: 89–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

