Trypanosoma cruzi-induced activation of functionally distinct αβ and γδ CD4- CD8- T cells in individuals with polar forms of Chagas' disease
- PMID: 20696836
- PMCID: PMC2950361
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00179-10
Trypanosoma cruzi-induced activation of functionally distinct αβ and γδ CD4- CD8- T cells in individuals with polar forms of Chagas' disease
Abstract
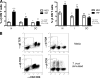
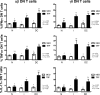
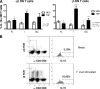
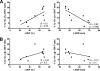
CD4(-) CD8(-) (double-negative [DN]) T cells have recently been shown to display important immunological functions in human diseases. They express γδ or αβ T-cell receptors that recognize lipid/glycolipid antigens presented via the nonclassical major histocompatibility complex molecules of the CD1 family. We recently demonstrated that while αβ DN T cells serve primarily to express inflammatory cytokines, γδ DN T cells express mainly interleukin-10 (IL-10) in patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis. We also demonstrated a correlation between DN T cells and the expression of gamma interferon in the acute phase of Trypanosoma cruzi experimental infection. In this work, we sought to investigate whether αβ or γδ DN T cells display distinct immunoregulatory potentials in patients with polar forms of human Chagas' disease. Our data showed that in vitro infection with T. cruzi leads to expansion of DN T cells in patients with the indeterminate and severe cardiac clinical forms of the disease. However, while αβ DN T cells primarily produce inflammatory cytokines in both forms of the disease, γδ DN T cells display a marked, significant increase in antigen-specific IL-10 expression in indeterminate patients relative to cardiac patients. Finally, higher frequencies of the IL-10-producing γδ DN T cells were correlated with improved clinical measures of cardiac function in the patients, suggesting a protective role for these cells in Chagas' disease. Taken together, these data show distinct functional characteristics for αβ and γδ DN T cells associated with distinct morbidity rates and clinical forms in human Chagas' disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Specific activation of CD4- CD8- double-negative T cells by Trypanosoma cruzi-derived glycolipids induces a proinflammatory profile associated with cardiomyopathy in Chagas patients.Clin Exp Immunol. 2017 Oct;190(1):122-132. doi: 10.1111/cei.12992. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28543170 Free PMC article.
-
CD4-CD8-αβ and γδ T cells display inflammatory and regulatory potentials during human tuberculosis.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50923. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050923. Epub 2012 Dec 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23239994 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct CD4-CD8- (Double-Negative) Memory T-Cell Subpopulations Are Associated With Indeterminate and Cardiac Clinical Forms of Chagas Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 11;12:761795. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.761795. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34868005 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological control of Trypanosoma cruzi infection and pathogenesis of Chagas' disease.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1997 Oct;114(2):103-10. doi: 10.1159/000237653. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9338602 Review.
-
Whodunit? The Contribution of Interleukin (IL)-17/IL-22-Producing γδ T Cells, αβ T Cells, and Innate Lymphoid Cells to the Pathogenesis of Spondyloarthritis.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 25;9:885. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00885. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29922283 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current understanding of immunity to Trypanosoma cruzi infection and pathogenesis of Chagas disease.Semin Immunopathol. 2012 Nov;34(6):753-70. doi: 10.1007/s00281-012-0351-7. Epub 2012 Oct 18. Semin Immunopathol. 2012. PMID: 23076807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Activation of Human Monocytes and Lymphocytes by Distinct Strains of Trypanosoma cruzi.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015 Jul 6;9(7):e0003816. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003816. eCollection 2015. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015. PMID: 26147698 Free PMC article.
-
Specific activation of CD4- CD8- double-negative T cells by Trypanosoma cruzi-derived glycolipids induces a proinflammatory profile associated with cardiomyopathy in Chagas patients.Clin Exp Immunol. 2017 Oct;190(1):122-132. doi: 10.1111/cei.12992. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28543170 Free PMC article.
-
Immune exhaustion in chronic Chagas disease: Pro-inflammatory and immunomodulatory action of IL-27 in vitro.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Jun 1;15(6):e0009473. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009473. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34061845 Free PMC article.
-
Low Double-Negative CD3+CD4-CD8- T Cells Are Associated with Incomplete Restoration of CD4+ T Cells and Higher Immune Activation in HIV-1 Immunological Non-Responders.Front Immunol. 2016 Dec 9;7:579. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00579. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 28018346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albareda, M. C., S. A. Laucella, M. G. Alvarez, A. H. Armenti, G. Bertochi, R. L. Tarleton, and M. Postan. 2006. Trypanosoma cruzi modulates the profile of memory CD8+ T cells in chronic Chagas' disease patients. Int. Immunol. 18:465-471. - PubMed
-
- Antonelli, L. R., W. O. Dutra, R. P. Almeida, O. Bacellar, E. M. Carvalho, and K. J. Gollob. 2005. Activated inflammatory T cells correlate with lesion size in human cutaneous leishmaniasis. Immunol. Lett. 101:226-230. - PubMed
-
- Araujo, F. F., J. A. Gomes, M. O. Rocha, S. Williams-Blangero, V. M. Pinheiro, M. J. Morato, and R. Correa-Oliveira. 2007. Potential role of CD4+ CD25HIGH regulatory T cells in morbidity in Chagas disease. Front Biosci. 12:2797-2806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

