T-Analyst: a program for efficient analysis of protein conformational changes by torsion angles
- PMID: 20689979
- PMCID: PMC2940022
- DOI: 10.1007/s10822-010-9376-y
T-Analyst: a program for efficient analysis of protein conformational changes by torsion angles
Abstract
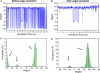
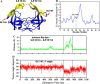
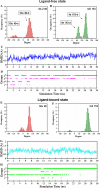
T-Analyst is a user-friendly computer program for analyzing trajectories from molecular modeling. Instead of using Cartesian coordinates for protein conformational analysis, T-Analyst is based on internal bond-angle-torsion coordinates in which internal torsion angle movements, such as side-chain rotations, can be easily detected. The program computes entropy and automatically detects and corrects angle periodicity to produce accurate rotameric states of dihedrals. It also clusters multiple conformations and detects dihedral rotations that contribute hinge-like motions. Correlated motions between selected dihedrals can also be observed from the correlation map. T-Analyst focuses on showing changes in protein flexibility between different states and selecting representative protein conformations for molecular docking studies. The program is provided with instructions and full source code in Perl.
Figures

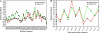
Similar articles
-
Can Conformational Changes of Proteins Be Represented in Torsion Angle Space? A Study with Rescaled Ridge Regression.J Chem Inf Model. 2019 Nov 25;59(11):4929-4941. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00627. Epub 2019 Oct 29. J Chem Inf Model. 2019. PMID: 31600071
-
EncoderMap(II): Visualizing Important Molecular Motions with Improved Generation of Protein Conformations.J Chem Inf Model. 2019 Nov 25;59(11):4550-4560. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00675. Epub 2019 Nov 5. J Chem Inf Model. 2019. PMID: 31647645
-
Statistical and conformational analysis of the electron density of protein side chains.Proteins. 2007 Feb 1;66(2):279-303. doi: 10.1002/prot.21150. Proteins. 2007. PMID: 17080462
-
Exploring structural variability in X-ray crystallographic models using protein local optimization by torsion-angle sampling.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2008 Apr;64(Pt 4):383-96. doi: 10.1107/S090744490800070X. Epub 2008 Mar 19. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2008. PMID: 18391405 Free PMC article.
-
Folding funnels and conformational transitions via hinge-bending motions.Cell Biochem Biophys. 1999;31(2):141-64. doi: 10.1007/BF02738169. Cell Biochem Biophys. 1999. PMID: 10593256 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights Into Dynamics of Inhibitor and Ubiquitin-Like Protein Binding in SARS-CoV-2 Papain-Like Protease.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Aug 4;7:174. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00174. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32850963 Free PMC article.
-
Agonist and antagonist binding to the nuclear vitamin D receptor: dynamics, mutation effects and functional implications.In Silico Pharmacol. 2013 Feb 12;1:2. doi: 10.1186/2193-9616-1-2. eCollection 2013. In Silico Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 25505647 Free PMC article.
-
Substitution of a Surface-Exposed Residue Involved in an Allosteric Network Enhances Tryptophan Synthase Function in Cells.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 26;8:679915. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.679915. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34124159 Free PMC article.
-
The role of oligomerization and cooperative regulation in protein function: the case of tryptophan synthase.PLoS Comput Biol. 2010 Nov 11;6(11):e1000994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000994. PLoS Comput Biol. 2010. PMID: 21085641 Free PMC article.
-
Achieving peptide binding specificity and promiscuity by loops: case of the forkhead-associated domain.PLoS One. 2014 May 28;9(5):e98291. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098291. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24870410 Free PMC article.

