Cross-reactivity of antibodies against leptospiral recurrent uveitis-associated proteins A and B (LruA and LruB) with eye proteins
- PMID: 20689825
- PMCID: PMC2914785
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000778
Cross-reactivity of antibodies against leptospiral recurrent uveitis-associated proteins A and B (LruA and LruB) with eye proteins
Abstract
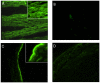
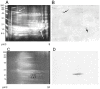
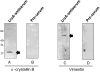
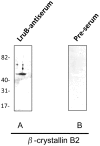
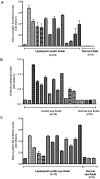
Infection by Leptospira interrogans has been causally associated with human and equine uveitis. Studies in our laboratories have demonstrated that leptospiral lipoprotein LruA and LruB are expressed in the eyes of uveitic horses, and that antibodies directed against LruA and LruB react with equine lenticular and retinal extracts, respectively. These reactivities were investigated further by performing immunofluorescent assays on lenticular and retinal tissue sections. Incubation of lens tissue sections with LruA-antiserum and retinal sections with LruB-antiserum resulted in positive fluorescence. By employing two-dimensional gel analyses followed by immunoblotting and mass spectrometry, lens proteins cross-reacting with LruA antiserum were identified to be alpha-crystallin B and vimentin. Similarly, mass spectrometric analyses identified beta-crystallin B2 as the retinal protein cross-reacting with LruB-antiserum. Purified recombinant human alpha-crystallin B and vimentin were recognized by LruA-directed antiserum, but not by control pre-immune serum. Recombinant beta-crystallin B2 was likewise recognized by LruB-directed antiserum, but not by pre-immune serum. Moreover, uveitic eye fluids contained significantly higher levels of antiibodies that recognized alpha-crystallin B, beta-crystallin B2 and vimentin than did normal eye fluids. Our results indicate that LruA and LruB share immuno-relevant epitopes with eye proteins, suggesting that cross-reactive antibody interactions with eye antigens may contribute to immunopathogenesis of Leptospira-associated recurrent uveitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LruA and LruB, novel lipoproteins of pathogenic Leptospira interrogans associated with equine recurrent uveitis.Infect Immun. 2005 Nov;73(11):7259-66. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.11.7259-7266.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16239521 Free PMC article.
-
LruA and LruB antibodies in sera of humans with leptospiral uveitis.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2008 Jun;15(6):1019-23. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00203-07. Epub 2008 Apr 9. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18400972 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Immunomodulators and immunosuppressants for multiple sclerosis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jun 6;2013(6):CD008933. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008933.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23744561 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Leptospirosis: risk factors and management challenges in developing countries.Res Rep Trop Med. 2016 Sep 28;7:49-62. doi: 10.2147/RRTM.S102543. eCollection 2016. Res Rep Trop Med. 2016. PMID: 30050339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibodies to a novel leptospiral protein, LruC, in the eye fluids and sera of horses with Leptospira-associated uveitis.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012 Mar;19(3):452-6. doi: 10.1128/CVI.05524-11. Epub 2012 Jan 11. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22237897 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into the Structure, Functions, and Dynamics of the Leptospira Outer Membrane Proteins with the Pathogenicity.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Mar 7;12(3):300. doi: 10.3390/membranes12030300. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35323775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Proteome Analysis Shows the Abundance of Histidine Kinase Sensor Protein, DNA Helicase, Putative Lipoprotein Containing Peptidase M75 Domain and Peptidase C39 Domain Protein in Leptospira interrogans Grown in EMJH Medium.Pathogens. 2021 Jul 6;10(7):852. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10070852. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34358002 Free PMC article.
-
Ex Vivo and In Vitro Analysis Identify a Detrimental Impact of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps on Eye Structures in Equine Recurrent Uveitis.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 10;13:830871. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.830871. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35251020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thiermann AB. Leptospirosis: Current developments and trends. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1984;184:722–725. - PubMed
-
- Vinetz JM. Leptospirosis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2001;14:527–538. - PubMed
-
- Faine S, Adler B, Bolin C, Perolat P. Leptospira and leptospirosis. Melbourne, Australia: MediSci; 1999.
-
- Rathinam SR. Ocular leptospirosis. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2002;13:381–386. - PubMed
-
- Errington BJ. Ophthalmology in Equidae. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1941;98:115–123.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

