CX3CL1-CX3CR1 interaction prevents carbon tetrachloride-induced liver inflammation and fibrosis in mice
- PMID: 20683935
- PMCID: PMC2947579
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.23795
CX3CL1-CX3CR1 interaction prevents carbon tetrachloride-induced liver inflammation and fibrosis in mice
Abstract
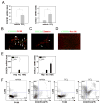
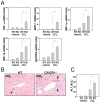
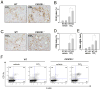
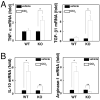
Chronic liver disease is associated with hepatocyte injury, inflammation, and fibrosis. Chemokines and chemokine receptors are key factors for the migration of inflammatory cells such as macrophages and noninflammatory cells such as hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). The expression of CX3CR1 and its ligand, CX3CL1, is up-regulated in chronic liver diseases such as chronic hepatitis C. However, the precise role of CX3CR1 in the liver is still unclear. Here we investigated the role of the CX3CL1-CX3CR1 interaction in a carbon tetrachloride (CCl(4))-induced liver inflammation and fibrosis model. CX3CR1 was dominantly expressed in Kupffer cells in the liver. In contrast, the main source of CX3CL1 was HSCs. Mice deficient in CX3CR1 showed significant increases in inflammatory cell recruitment and cytokine production [including tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α); monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; macrophage inflammatory protein 1β; and regulated upon activation, normal T cell expressed, and secreted (RANTES)] after CCl(4) treatment versus wild-type (WT) mice. This suggested that CX3CR1 signaling prevented liver inflammation. Kupffer cells in CX3CR1-deficient mice after CCl(4) treatment showed increased expression of TNF-α and transforming growth factor β and reduced expression of the anti-inflammatory markers interleukin-10 (IL-10) and arginase-1. Coculture experiments showed that HSCs experienced significantly greater activation by Kupffer cells from CCl(4)-treated CX3CR1-deficient mice versus WT mice. Indeed, augmented fibrosis was observed in CX3CR1-deficient mice versus WT mice after CCl(4) treatment. Finally, CX3CL1 treatment induced the expression of IL-10 and arginase-1 in WT cultured Kupffer cells through CX3CR1, which in turn suppressed HSC activation.
Conclusion: The CX3CL1-CX3CR1 interaction inhibits inflammatory properties in Kupffer cells/macrophages and results in decreased liver inflammation and fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CX3CR1 deficiency attenuates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation with decreased M1 macrophages.J Dermatol Sci. 2016 Jun;82(3):175-88. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2016.03.004. Epub 2016 Mar 4. J Dermatol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26976687
-
CX3CR1 deficiency exacerbates immune-mediated hepatitis by increasing NF-κB-mediated cytokine production in macrophage and T cell.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023 Jan;248(2):117-129. doi: 10.1177/15353702221128573. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023. PMID: 36426712 Free PMC article.
-
CX3CL1-CX3CR1 interaction mediates macrophage-mesothelial cross talk and promotes peritoneal fibrosis.Kidney Int. 2019 Jun;95(6):1405-1417. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.12.030. Epub 2019 Mar 5. Kidney Int. 2019. PMID: 30948201
-
Fractalkine (CX3CL1) and Its Receptor CX3CR1: A Promising Therapeutic Target in Chronic Kidney Disease?Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 7;12:664202. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.664202. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34163473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The chemokine CX3CL1 (fractalkine) and its receptor CX3CR1: occurrence and potential role in osteoarthritis.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2014 Oct;62(5):395-403. doi: 10.1007/s00005-014-0275-0. Epub 2014 Feb 21. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2014. PMID: 24556958 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional role of chemokines in liver disease models.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Dec;7(12):682-90. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.168. Epub 2010 Oct 26. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 20975742 Review.
-
The M2 polarization of macrophage induced by fractalkine in the endometriotic milieu enhances invasiveness of endometrial stromal cells.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013 Dec 15;7(1):194-203. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013. PMID: 24427339 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted role of macrophages during acute liver injury.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 6;14:1237042. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1237042. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37736102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemokines in chronic liver allograft dysfunction pathogenesis and potential therapeutic targets.Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:325318. doi: 10.1155/2013/325318. Epub 2013 Dec 8. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24382971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Expression of CX3CL1 in Hepatitis B Virus-Replicating Hepatoma Cells Can Affect the Migration Activity of CX3CR1+ Immune Cells.J Virol. 2015 Jul;89(14):7016-27. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00716-15. Epub 2015 Apr 29. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25926643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crispe IN. The liver as a lymphoid organ. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:147–163. - PubMed
-
- Tacke F, Luedde T, Trautwein C. Inflammatory pathways in liver homeostasis and liver injury. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2009;36:4–12. - PubMed
-
- Seki E, De Minicis S, Osterreicher CH, Kluwe J, Osawa Y, Brenner DA, Schwabe RF. TLR4 enhances TGF-beta signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat Med. 2007;13:1324–1332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
