Evaluation and ranking of enzyme designs
- PMID: 20665693
- PMCID: PMC2975139
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.462
Evaluation and ranking of enzyme designs
Abstract
In 2008, a successful computational design procedure was reported that yielded active enzyme catalysts for the Kemp elimination. Here, we studied these proteins together with a set of previously unpublished inactive designs to determine the sources of activity or lack thereof, and to predict which of the designed structures are most likely to be catalytic. Methods that range from quantum mechanics (QM) on truncated model systems to the treatment of the full protein with ONIOM QM/MM and AMBER molecular dynamics (MD) were explored. The most effective procedure involved molecular dynamics, and a general MD protocol was established. Substantial deviations from the ideal catalytic geometries were observed for a number of designs. Penetration of water into the catalytic site and insufficient residue-packing around the active site are the main factors that can cause enzyme designs to be inactive. Where in the past, computational evaluations of designed enzymes were too time-extensive for practical considerations, it has now become feasible to rank and refine candidates computationally prior to and in conjunction with experimentation, thus markedly increasing the efficiency of the enzyme design process.
Copyright © 2010 The Protein Society.
Figures
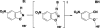
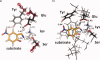

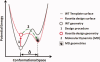
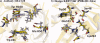
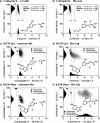
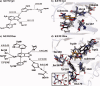
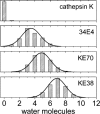
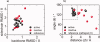
Similar articles
-
Molecular dynamics explorations of active site structure in designed and evolved enzymes.Acc Chem Res. 2015 Apr 21;48(4):1080-9. doi: 10.1021/ar500452q. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Acc Chem Res. 2015. PMID: 25738880
-
Hybrid schemes based on quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics simulations goals to success, problems, and perspectives.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2011;85:81-142. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386485-7.00003-X. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2011. PMID: 21920322 Review.
-
Catalytic mechanism and performance of computationally designed enzymes for Kemp elimination.J Am Chem Soc. 2008 Nov 26;130(47):15907-15. doi: 10.1021/ja804040s. J Am Chem Soc. 2008. PMID: 18975945 Free PMC article.
-
A preorganization oriented computational method for de novo design of Kemp elimination enzymes.Enzyme Microb Technol. 2022 Oct;160:110093. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2022.110093. Epub 2022 Jul 2. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2022. PMID: 35816919
-
Combined quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) methods in computational enzymology.Biochemistry. 2013 Apr 23;52(16):2708-28. doi: 10.1021/bi400215w. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23557014 Review.
Cited by
-
Enzyme informatics.Curr Top Med Chem. 2012;12(17):1911-23. doi: 10.2174/156802612804547353. Curr Top Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 23116471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative structural insight into human variegate porphyria disease.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 26;288(17):11731-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.459768. Epub 2013 Mar 6. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23467411 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing a de novo enzyme activity by computationally-focused ultra-low-throughput screening.Chem Sci. 2020 May 19;11(24):6134-6148. doi: 10.1039/d0sc01935f. eCollection 2020 Jun 28. Chem Sci. 2020. PMID: 32832059 Free PMC article.
-
Computational design of catalytic dyads and oxyanion holes for ester hydrolysis.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Oct 3;134(39):16197-206. doi: 10.1021/ja3037367. Epub 2012 Sep 21. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22871159 Free PMC article.
-
Computational design of serine hydrolases.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 30:2024.08.29.610411. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.29.610411. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39257749 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Fersht AR. Structure and mechanism in protein science. New York: W.H. Freeman and Co; 2002.
-
- Gouverneur VE, Houk KN, Pascual-Teresa BD, Beno B, Janda KD, Lerner RA. Control of the exo and endo pathways of the Diels-Alder reaction by antibody catalysis. Science. 1993;262:204–208. - PubMed
-
- Thorn SN, Daniels RG, Auditor MM, Hilvert D. Large rate accelerations in antibody catalysis by strategic use of haptenic charge. Nature. 1995;373:228–230. - PubMed
-
- Wagner J, Lerner RA, Barbas CF., III Efficient aldolase catalytic antibodies that use the enamine mechanism of natural enzymes. Science. 1995;270:1797–1800. - PubMed
-
- Kikuchi K, Hannak RB, Guo M, Kirby AJ, Hilvert D. Toward bifunctional antibody catalysis. Bioorg Med Chem. 2006;14:6189–6196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

