I-motif structures formed in the human c-MYC promoter are highly dynamic--insights into sequence redundancy and I-motif stability
- PMID: 20657837
- PMCID: PMC2906509
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011647
I-motif structures formed in the human c-MYC promoter are highly dynamic--insights into sequence redundancy and I-motif stability
Abstract
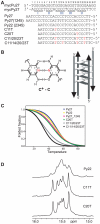
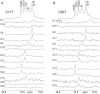
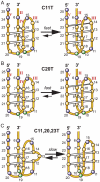
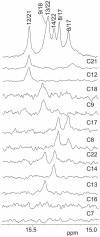
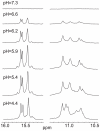
The GC-rich nuclease hypersensitivity element III1 (NHE III1) of the c-MYC promoter largely controls the transcriptional activity of the c-MYC oncogene. The C-rich strand in this region can form I-motif DNA secondary structures. We determined the folding pattern of the major I-motif formed in the NHE III1, which can be formed at near-neutral pH. While we find that the I-motif formed in the four 3' consecutive runs of cytosines appears to be the most favored, our results demonstrate that the C-rich strand of the c-MYC NHE III1 exhibits a high degree of dynamic equilibration. Using a trisubstituted oligomer of this region, we determined the formation of two equilibrating loop isomers, one of which contains a flipped-out cytosine. Our results indicate that the intercalative cytosine+-cytosine base pairs are not always necessary for an intramolecular I-motif. The dynamic character of the c-MYC I-motif is intrinsic to the NHE III1 sequence and appears to provide stability to the c-MYC I-motif.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
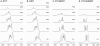
Similar articles
-
The flanking sequence contributes to the immobilisation of spermine at the G-quadruplex in the NHE (nuclease hypersensitivity element) III1 of the c-Myc promoter.FEBS Lett. 2014 May 21;588(10):1949-54. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.04.003. Epub 2014 Apr 13. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24735723
-
Structure of the biologically relevant G-quadruplex in the c-MYC promoter.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2006;25(8):951-68. doi: 10.1080/15257770600809913. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2006. PMID: 16901825 Review.
-
Molecular modeling and biophysical analysis of the c-MYC NHE-III1 silencer element.J Mol Model. 2008 Feb;14(2):93-101. doi: 10.1007/s00894-007-0254-z. Epub 2007 Dec 18. J Mol Model. 2008. PMID: 18087730
-
Thermodynamic stability and folding kinetics of the major G-quadruplex and its loop isomers formed in the nuclease hypersensitive element in the human c-Myc promoter: effect of loops and flanking segments on the stability of parallel-stranded intramolecular G-quadruplexes.Biochemistry. 2010 Nov 2;49(43):9152-60. doi: 10.1021/bi100946g. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20849082 Free PMC article.
-
Drug targeting of the c-MYC promoter to repress gene expression via a G-quadruplex silencer element.Semin Oncol. 2006 Aug;33(4):498-512. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2006.04.012. Semin Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16890804 Review.
Cited by
-
Opposite Effects of Potassium Ions on the Thermal Stability of i-Motif DNA in Different Buffer Systems.ACS Omega. 2021 Mar 24;6(13):8976-8985. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c06350. eCollection 2021 Apr 6. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 33842768 Free PMC article.
-
A pH-dependent bolt involving cytosine bases located in the lateral loops of antiparallel G-quadruplex structures within the SMARCA4 gene promotor.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 1;9(1):15807. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52311-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31676783 Free PMC article.
-
The i-Motif as a Molecular Target: More Than a Complementary DNA Secondary Structure.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Jan 27;14(2):96. doi: 10.3390/ph14020096. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33513764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting DNA G-quadruplex structures with peptide nucleic acids.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(14):1984-91. doi: 10.2174/138161212799958440. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22376112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic modification of cytosines fine tunes the stability of i-motif DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jan 10;48(1):55-62. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1082. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31777919 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marcu KB, Bossone SA, Patel AJ. myc Function and Regulation. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 1992;61:809–858. - PubMed
-
- Pelengaris S, Rudolph B, Littlewood T. Action of Myc in vivo — proliferation and apoptosis. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 2000;10:100–105. - PubMed
-
- Pelengaris S, Khan M. The c-MYC oncoprotein as a treatment target in cancer and other disorders of cell growth. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets. 2003;7:623–642. - PubMed
-
- Spencer CA, Groudine M. Control of c-myc regulation in normal and neoplastic cells. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;56:1–48. - PubMed
-
- Magrath I. The pathogenesis of Burkitt's lymphoma. Advances in Cancer Research. 1990;55:133–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

