Targeting the dynamic HSP90 complex in cancer
- PMID: 20651736
- PMCID: PMC6778733
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc2887
Targeting the dynamic HSP90 complex in cancer
Abstract
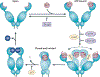
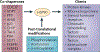
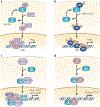
The molecular chaperone heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) has been used by cancer cells to facilitate the function of numerous oncoproteins, and it can be argued that cancer cells are 'addicted' to HSP90. However, although recent reports of the early clinical efficacy of HSP90 inhibitors are encouraging, the optimal use of HSP90-targeted therapeutics will depend on understanding the complexity of HSP90 regulation and the degree to which HSP90 participates in both neoplastic and normal cellular physiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structure, function and regulation of the hsp90 machinery.Biomed J. 2013 May-Jun;36(3):106-17. doi: 10.4103/2319-4170.113230. Biomed J. 2013. PMID: 23806880 Review.
-
Impact of Posttranslational Modifications on the Anticancer Activity of Hsp90 Inhibitors.Adv Cancer Res. 2016;129:31-50. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Adv Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26916000 Review.
-
Targeting Hsp90 in urothelial carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 20;6(11):8454-73. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3502. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25909217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting HSP90 for cancer therapy.Br J Cancer. 2009 May 19;100(10):1523-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605066. Epub 2009 Apr 28. Br J Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19401686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New developments in Hsp90 inhibitors as anti-cancer therapeutics: mechanisms, clinical perspective and more potential.Drug Resist Updat. 2009 Feb-Apr;12(1-2):17-27. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2008.12.002. Drug Resist Updat. 2009. PMID: 19179103 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Programmable "triple attack" cancer therapy through in situ activation of disulfiram toxification combined with phototherapeutics.Chem Sci. 2024 Jun 14;15(29):11633-11642. doi: 10.1039/d3sc05300h. eCollection 2024 Jul 24. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 39055020 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp90 inhibitors are efficacious against Kaposi Sarcoma by enhancing the degradation of the essential viral gene LANA, of the viral co-receptor EphA2 as well as other client proteins.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(11):e1003048. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003048. Epub 2012 Nov 29. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23209418 Free PMC article.
-
Cranial Neural Crest Cells and Their Role in the Pathogenesis of Craniofacial Anomalies and Coronal Craniosynostosis.J Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 9;8(3):18. doi: 10.3390/jdb8030018. J Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32916911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulforaphane attenuates EGFR signaling in NSCLC cells.J Biomed Sci. 2015 Jun 3;22(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12929-015-0139-x. J Biomed Sci. 2015. PMID: 26036303 Free PMC article.
-
Increased radiosensitivity and radiothermosensitivity of human pancreatic MIA PaCa-2 and U251 glioblastoma cell lines treated with the novel Hsp90 inhibitor NVP-HSP990.Radiat Oncol. 2013 Feb 28;8:42. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-8-42. Radiat Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23448094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wandinger SK, Richter K. & Buchner J. The Hsp90 chaperone machinery. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 18473–18477 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Zhao R. et al. Navigating the chaperone network: an integrative map of physical and genetic interactions mediated by the hsp90 chaperone. Cell 120, 715–727 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Pratt WB & Toft DO Regulation of signaling protein function and trafficking by the hsp90/hsp70-based chaperone machinery. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 228, 111–133 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Whitesell L. & Lindquist SL HSP90 and the chaperoning of cancer. Nature Rev. Cancer 5, 761–772 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Dezwaan DC & Freeman BC HSP90: the Rosetta stone for cellular protein dynamics? Cell Cycle 7, 1006–1012 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

