Argonaute 2 in dopamine 2 receptor-expressing neurons regulates cocaine addiction
- PMID: 20643829
- PMCID: PMC2931161
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20100451
Argonaute 2 in dopamine 2 receptor-expressing neurons regulates cocaine addiction
Abstract
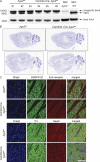
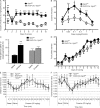
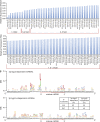
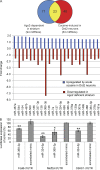
Cocaine is a highly addictive drug that exerts its effects by increasing the levels of released dopamine in the striatum, followed by stable changes in gene transcription, mRNA translation, and metabolism within medium spiny neurons in the striatum. The multiple changes in gene and protein expression associated with cocaine addiction suggest the existence of a mechanism that facilitates a coordinated cellular response to cocaine. Here, we provide evidence for a key role of miRNAs in cocaine addiction. We show that Argonaute 2 (Ago2), which plays an important role in miRNA generation and execution of miRNA-mediated gene silencing, is involved in regulation of cocaine addiction. Deficiency of Ago2 in dopamine 2 receptor (Drd2)-expressing neurons greatly reduces the motivation to self-administer cocaine in mice. We identified a distinct group of miRNAs that is specifically regulated by Ago2 in the striatum. Comparison of miRNAs affected by Ago2 deficiency with miRNAs that are enriched and/or up-regulated in Drd2-neurons in response to cocaine identified a set of miRNAs that are likely to play a role in cocaine addiction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute binge pattern cocaine administration induces region-specific effects in D1-r- and D2-r-expressing cells in eGFP transgenic mice.Neuroscience. 2013 Dec 3;253:123-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.08.032. Epub 2013 Aug 31. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 24001687
-
Histone arginine methylation in cocaine action in the nucleus accumbens.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Aug 23;113(34):9623-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1605045113. Epub 2016 Aug 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27506785 Free PMC article.
-
Stress and addiction: glucocorticoid receptor in dopaminoceptive neurons facilitates cocaine seeking.Nat Neurosci. 2009 Mar;12(3):247-9. doi: 10.1038/nn.2282. Epub 2009 Feb 22. Nat Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19234455
-
Molecular, cellular, and structural mechanisms of cocaine addiction: a key role for microRNAs.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Jan;38(1):198-211. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.120. Epub 2012 Sep 12. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 22968819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cocaine-induced metaplasticity in the nucleus accumbens: silent synapse and beyond.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Dec;61(7):1060-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.12.033. Epub 2011 Jan 11. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21232547 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Big (sequencing) future of non-coding RNA research for the understanding of cocaine.Front Genet. 2012 Sep 3;3:158. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00158. eCollection 2012. Front Genet. 2012. PMID: 22969790 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Repeat variation in the human PER2 gene as a new genetic marker associated with cocaine addiction and brain dopamine D2 receptor availability.Transl Psychiatry. 2012 Mar 6;2(3):e86. doi: 10.1038/tp.2012.11. Transl Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22832851 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA receptor-dependent regulation of miRNA expression and association with Argonaute during LTP in vivo.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Jan 13;7:285. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00285. eCollection 2014 Jan 13. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24454279 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in neuronal communication.Mol Neurobiol. 2014 Jun;49(3):1309-26. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8603-7. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Mol Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24385256 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in opioid pharmacology.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012 Dec;7(4):808-19. doi: 10.1007/s11481-011-9323-2. Epub 2011 Nov 9. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22068836 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

