Deletions and mutations in the acidic lipid-binding region of the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump: a study on different splicing variants of isoform 2
- PMID: 20643655
- PMCID: PMC2945572
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.140475
Deletions and mutations in the acidic lipid-binding region of the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump: a study on different splicing variants of isoform 2
Abstract
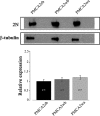
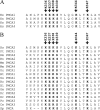
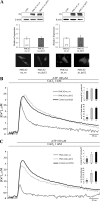
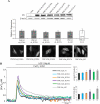
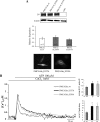
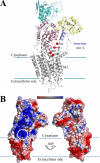
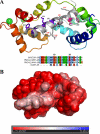
Acidic phospholipids increase the affinity of the plasma membrane Ca(2+)-ATPase pump for Ca(2+). They interact with the C-terminal region of the pump and with a domain in the loop connecting transmembrane domains 2 and 3 (A(L) region) next to site A of alternative splicing. The contribution of the two phospholipid-binding sites and the possible interference of splicing inserts at site A with the regulation of the ATPase activity of isoform 2 of the pump by phospholipids have been analyzed. The activity of the full-length z/b variant (no insert at site A), the w/b (with insert at site A), and the w/a variant, containing both the 45-amino acid A-site insert and a C-site insert that truncates the pump in the calmodulin binding domain, has been analyzed in microsomal membranes of overexpressing CHO cells. The A-site insertion did not modify the phospholipid sensitivity of the pump, but the doubly inserted w/a variant became insensitive to acidic phospholipids, even if containing the intact A(L) phospholipid binding domain. Pump mutants in which 12 amino acids had been deleted, or single lysine mutations introduced, in the A(L) region were studied by monitoring agonist-induced Ca(2+) transients in overexpressing CHO cells. The 12-residue deletion completely abolished the ATPase activity of the w/a variant but only reduced that of the z/b variant, which was also affected by the single lysine substitutions in the same domain. A structural interpretation of the interplay of the pump with phospholipids, and of the mechanism of their activation, is proposed on the basis of molecular modeling studies.
Figures

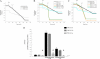

Similar articles
-
Deletions in the A(L) region of the h4xb plasma membrane Ca(2+) pump. High apparent affinity for Ca(2+) of a deletion mutant resembling the alternative spliced form h4zb.FEBS Lett. 2006 Mar 6;580(6):1576-80. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.01.088. Epub 2006 Feb 3. FEBS Lett. 2006. PMID: 16488415
-
The plasma membrane calcium pump in the hearing process: physiology and pathology.Sci China Life Sci. 2011 Aug;54(8):686-90. doi: 10.1007/s11427-011-4200-z. Epub 2011 Jul 24. Sci China Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21786191 Review.
-
Deletions in the acidic lipid-binding region of the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump. A mutant with high affinity for Ca2+ resembling the acidic lipid-activated enzyme.J Biol Chem. 2002 Apr 12;277(15):12784-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111055200. Epub 2002 Jan 30. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11821403
-
Determination of the dissociation constants for Ca2+ and calmodulin from the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump by a lipid probe that senses membrane domain changes.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 1;285(1):123-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.076679. Epub 2009 Nov 5. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19892708 Free PMC article.
-
Role of alternative splicing in generating isoform diversity among plasma membrane calcium pumps.Physiol Rev. 2001 Jan;81(1):21-50. doi: 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.1.21. Physiol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11152753 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Membrane Calcium Transport Proteins by the Surrounding Lipid Environment.Biomolecules. 2019 Sep 20;9(10):513. doi: 10.3390/biom9100513. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31547139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Factors in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Preliminary Experience with Whole Exome Sequencing.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 15;21(24):9551. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249551. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33333988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specific Activation of the Plant P-type Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase by Lysophospholipids Depends on the Autoinhibitory N- and C-terminal Domains.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 26;290(26):16281-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.617746. Epub 2015 May 13. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25971968 Free PMC article.
-
Sorcin Activates the Brain PMCA and Blocks the Inhibitory Effects of Molecular Markers of Alzheimer's Disease on the Pump Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 3;22(11):6055. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116055. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34205207 Free PMC article.
-
The plasma membrane calcium pump: new ways to look at an old enzyme.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 11;289(15):10261-10268. doi: 10.1074/jbc.O114.555565. Epub 2014 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24570005 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brini M., Coletto L., Pierobon N., Kraev N., Guerini D., Carafoli E. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 24500–24508 - PubMed
-
- Brini M., Carafoli E. (2009) Physiol. Rev. 89, 1341–1378 - PubMed
-
- Rimessi A., Coletto L., Pinton P., Rizzuto R., Brini M., Carafoli E. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280, 37195–37203 - PubMed
-
- Linde C. I., Di Leva F., Domi T., Tosatto S. C., Brini M., Carafoli E. (2008) Cell Calcium 43, 550–561 - PubMed
-
- Chicka M. C., Strehler E. E. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 18464–18470 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

