Differential requirements for clathrin-dependent endocytosis at sites of cell-substrate adhesion
- PMID: 20631253
- PMCID: PMC2929999
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E09-12-1044
Differential requirements for clathrin-dependent endocytosis at sites of cell-substrate adhesion
Abstract
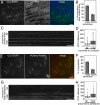
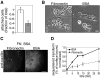
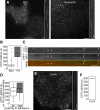
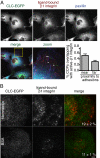
Clathrin-dependent endocytosis is a major route for the cellular import of macromolecules and occurs at the interface between the cell and its surroundings. However, little is known about the influences of cell-substrate attachment in clathrin-coated vesicle formation. Using biochemical and imaging-based methods, we find that cell-substrate adhesion reduces the rate of endocytosis. Clathrin-coated pits (CCPs) in proximity to substrate contacts exhibit slower dynamics in comparison to CCPs found more distant from adhesions. Direct manipulation of the extracellular matrix (ECM) to modulate adhesion demonstrates that tight adhesion dramatically reduces clathrin-dependent endocytosis and extends the lifetimes of clathrin structures. This reduction is in part mediated by integrin-matrix engagement. In addition, we demonstrate that actin cytoskeletal dynamics are differentially required for efficient endocytosis, with a stronger requirement for actin polymerization in areas of adhesion. Together, these results reveal that cell-substrate adhesion regulates clathrin-dependent endocytosis and suggests that actin assembly facilitates vesicle formation at sites of adhesion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cargo regulates clathrin-coated pit dynamics.Cell. 2006 Oct 6;127(1):113-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.08.035. Cell. 2006. PMID: 17018281
-
N-WASP deficiency impairs EGF internalization and actin assembly at clathrin-coated pits.J Cell Sci. 2005 Jul 15;118(Pt 14):3103-15. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02444. Epub 2005 Jun 28. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 15985465
-
Clathrin hub expression dissociates the actin-binding protein Hip1R from coated pits and disrupts their alignment with the actin cytoskeleton.Traffic. 2001 Nov;2(11):851-8. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2001.21114.x. Traffic. 2001. PMID: 11733052
-
Clathrin coated pits, plaques and adhesion.J Struct Biol. 2016 Oct;196(1):48-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2016.07.009. Epub 2016 Jul 16. J Struct Biol. 2016. PMID: 27431447 Review.
-
Understanding living clathrin-coated pits.Traffic. 2004 May;5(5):327-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9219.2004.00187.x. Traffic. 2004. PMID: 15086782 Review.
Cited by
-
The Plasma Membrane and Mechanoregulation in Cells.ACS Omega. 2024 May 13;9(20):21780-21797. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c01962. eCollection 2024 May 21. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38799362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane mechanics govern spatiotemporal heterogeneity of endocytic clathrin coat dynamics.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Nov 15;28(24):3480-3488. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-05-0282. Epub 2017 Sep 13. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28904210 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic interplay between cell membrane tension and clathrin-mediated endocytosis.Biol Cell. 2021 Aug;113(8):344-373. doi: 10.1111/boc.202000110. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33788963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type-I myosins promote actin polymerization to drive membrane bending in endocytosis.Elife. 2019 Aug 6;8:e44215. doi: 10.7554/eLife.44215. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31385806 Free PMC article.
-
Regarding the amazing choreography of clathrin coats.PLoS Biol. 2011 Mar;9(3):e1001037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001037. Epub 2011 Mar 22. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21445329 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Benesch S., Polo S., Lai F. P., Anderson K. I., Stradal T. E., Wehland J., Rottner K. N-WASP deficiency impairs EGF internalization and actin assembly at clathrin-coated pits. J. Cell Sci. 2005;118:3103–3115. - PubMed
-
- Blanpied T. A., Scott D. B., Ehlers M. D. Dynamics and regulation of clathrin coats at specialized endocytic zones of dendrites and spines. Neuron. 2002;36:435–449. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

