Evaluation of algorithm performance in ChIP-seq peak detection
- PMID: 20628599
- PMCID: PMC2900203
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011471
Evaluation of algorithm performance in ChIP-seq peak detection
Abstract
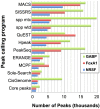
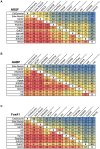
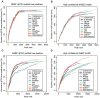
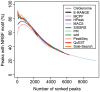
Next-generation DNA sequencing coupled with chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP-seq) is revolutionizing our ability to interrogate whole genome protein-DNA interactions. Identification of protein binding sites from ChIP-seq data has required novel computational tools, distinct from those used for the analysis of ChIP-Chip experiments. The growing popularity of ChIP-seq spurred the development of many different analytical programs (at last count, we noted 31 open source methods), each with some purported advantage. Given that the literature is dense and empirical benchmarking challenging, selecting an appropriate method for ChIP-seq analysis has become a daunting task. Herein we compare the performance of eleven different peak calling programs on common empirical, transcription factor datasets and measure their sensitivity, accuracy and usability. Our analysis provides an unbiased critical assessment of available technologies, and should assist researchers in choosing a suitable tool for handling ChIP-seq data.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Is this the right normalization? A diagnostic tool for ChIP-seq normalization.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 May 9;16:150. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0579-z. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25957089 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation and High-Throughput Sequencing (ChIP-Seq): Tips and Tricks Regarding the Laboratory Protocol and Initial Downstream Data Analysis.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1767:271-288. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7774-1_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29524141
-
Comprehensive assessment of differential ChIP-seq tools guides optimal algorithm selection.Genome Biol. 2022 May 24;23(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s13059-022-02686-y. Genome Biol. 2022. PMID: 35606795 Free PMC article.
-
[Processing and analysis of ChIP-seq data].Yi Chuan. 2012 Jun;34(6):773-83. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2012.00773. Yi Chuan. 2012. PMID: 22698750 Review. Chinese.
-
Computation for ChIP-seq and RNA-seq studies.Nat Methods. 2009 Nov;6(11 Suppl):S22-32. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1371. Nat Methods. 2009. PMID: 19844228 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Accounting for immunoprecipitation efficiencies in the statistical analysis of ChIP-seq data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2013 May 30;14:169. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-169. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23721376 Free PMC article.
-
Uniform, optimal signal processing of mapped deep-sequencing data.Nat Biotechnol. 2013 Jul;31(7):615-22. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2596. Epub 2013 Jun 16. Nat Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23770639
-
SATB1-mediated functional packaging of chromatin into loops.Methods. 2012 Nov;58(3):243-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.06.019. Epub 2012 Jul 7. Methods. 2012. PMID: 22782115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A workflow for genome-wide mapping of archaeal transcription factors with ChIP-seq.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 May;40(10):e74. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks063. Epub 2012 Feb 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22323522 Free PMC article.
-
Processing and analyzing ChIP-seq data: from short reads to regulatory interactions.Brief Funct Genomics. 2010 Dec;9(5-6):466-76. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elq022. Epub 2010 Sep 22. Brief Funct Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20861161 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

