Myeloid cells, BAFF, and IFN-gamma establish an inflammatory loop that exacerbates autoimmunity in Lyn-deficient mice
- PMID: 20624892
- PMCID: PMC2916124
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20100086
Myeloid cells, BAFF, and IFN-gamma establish an inflammatory loop that exacerbates autoimmunity in Lyn-deficient mice
Abstract
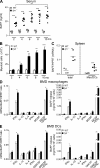
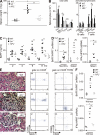
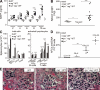
Autoimmunity is traditionally attributed to altered lymphoid cell selection and/or tolerance, whereas the contribution of innate immune cells is less well understood. Autoimmunity is also associated with increased levels of B cell-activating factor of the TNF family (BAFF; also known as B lymphocyte stimulator), a cytokine that promotes survival of self-reactive B cell clones. We describe an important role for myeloid cells in autoimmune disease progression. Using Lyn-deficient mice, we show that overproduction of BAFF by hyperactive myeloid cells contributes to inflammation and autoimmunity in part by acting directly on T cells to induce the release of IFN-gamma. Genetic deletion of IFN-gamma or reduction of BAFF activity, achieved by either reducing myeloid cell hyperproduction or by treating with an anti-BAFF monoclonal antibody, reduced disease development in lyn(-/-) mice. The increased production of IFN-gamma in lyn(-/-) mice feeds back on the myeloid cells to further stimulate BAFF release. Expression of BAFF receptor on T cells was required for their full activation and IFN-gamma release. Overall, our data suggest that the reciprocal production of BAFF and IFN-gamma establishes an inflammatory loop between myeloid cells and T cells that exacerbates autoimmunity in this model. Our findings uncover an important pathological role of BAFF in autoimmune disorders.
Figures
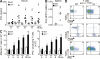

Similar articles
-
BAFF regulates activation of self-reactive T cells through B-cell dependent mechanisms and mediates protection in NOD mice.Eur J Immunol. 2014 Apr;44(4):983-93. doi: 10.1002/eji.201344186. Epub 2014 Feb 16. Eur J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24435807
-
The receptor tyrosine kinase MerTK regulates dendritic cell production of BAFF.Autoimmunity. 2009 Mar;42(3):183-97. doi: 10.1080/08916930802668586. Autoimmunity. 2009. PMID: 19301199 Free PMC article.
-
Development of autoimmune nephritis in genetically asplenic and splenectomized BAFF transgenic mice.J Autoimmun. 2011 Mar;36(2):125-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2010.12.002. Epub 2011 Jan 7. J Autoimmun. 2011. PMID: 21216131
-
Regulation of B cell self-tolerance by BAFF.Semin Immunol. 2006 Oct;18(5):276-83. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2006.04.003. Epub 2006 Aug 17. Semin Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16916609 Review.
-
B cells flying solo.Immunol Cell Biol. 2008 Jan;86(1):40-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.icb.7100142. Immunol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18172443 Review.
Cited by
-
Unbiased modifier screen reveals that signal strength determines the regulatory role murine TLR9 plays in autoantibody production.J Immunol. 2015 Apr 15;194(8):3675-86. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500026. Epub 2015 Mar 13. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25769918 Free PMC article.
-
The rationale for BAFF inhibition in systemic lupus erythematosus.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2012 Aug;14(4):295-302. doi: 10.1007/s11926-012-0258-2. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22535567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophils contribute to excess serum BAFF levels and promote CD4+ T cell and B cell responses in lupus-prone mice.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 10;9(7):e102284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102284. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25010693 Free PMC article.
-
T-bet-expressing B cells contribute to the autoreactive plasma cell pool in Lyn-/- mice.Eur J Immunol. 2023 Aug;53(8):e2250300. doi: 10.1002/eji.202250300. Epub 2023 May 14. Eur J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37134326 Free PMC article.
-
Readapting the adaptive immune response - therapeutic strategies for atherosclerosis.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Nov;174(22):3926-3939. doi: 10.1111/bph.13700. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28052311 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cash H., Relle M., Menke J., Brochhausen C., Jones S.A., Topley N., Galle P.R., Schwarting A. 2010. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) deficiency delays lupus nephritis in MRL-Faslpr mice: the IL-6 pathway as a new therapeutic target in treatment of autoimmune kidney disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 37:60–70 10.3899/jrheum.090194 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

