The Epstein-Barr virus-encoded G protein-coupled receptor BILF1 hetero-oligomerizes with human CXCR4, scavenges Gαi proteins, and constitutively impairs CXCR4 functioning
- PMID: 20622011
- PMCID: PMC2937994
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.115618
The Epstein-Barr virus-encoded G protein-coupled receptor BILF1 hetero-oligomerizes with human CXCR4, scavenges Gαi proteins, and constitutively impairs CXCR4 functioning
Abstract
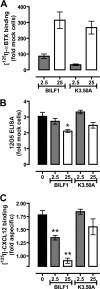
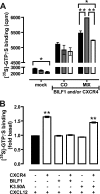
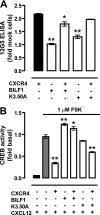
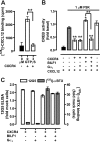
Cells express distinct G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) subtypes on their surface, allowing them to react to a corresponding variety of extracellular stimuli. Cross-regulation between different ligand-GPCR pairs is essential to generate appropriate physiological responses. GPCRs can physically affect each other's functioning by forming heteromeric complexes, whereas cross-regulation between activated GPCRs also occurs through integration of shared intracellular signaling networks. Human herpesviruses utilize virally encoded GPCRs to hijack cellular signaling networks for their own benefit. Previously, we demonstrated that the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded GPCR BILF1 forms heterodimeric complexes with human chemokine receptors. Using a combination of bimolecular complementation and bioluminescence resonance energy transfer approaches, we now show the formation of hetero-oligomeric complexes between this viral GPCR and human CXCR4. BILF1 impaired CXCL12 binding to CXCR4 and, consequently, also CXCL12-induced signaling. In contrast, the G protein uncoupled mutant BILF1-K(3.50)A affected CXCL12-induced CXCR4 signaling to a much lesser extent, indicating that BILF1-mediated CXCR4 inhibition is a consequence of its constitutive activity. Co-expression of Gα(i1) with BILF1 and CXCR4 restored CXCL12-induced signaling. Likewise, BILF1 formed heteromers with the human histamine H(4) receptor (H(4)R). BILF1 inhibited histamine-induced Gα(i)-mediated signaling by H(4)R, however, without affecting histamine binding to this receptor. These data indicate that functional cross-regulation of Gα(i)-coupled GPCRs by BILF1 is at the level of G proteins, even though these GPCRs are assembled in hetero-oligomeric complexes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded BILF1 is a constitutively active G protein-coupled receptor.J Virol. 2005 Jan;79(1):536-46. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.1.536-546.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15596846 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct Roles of Extracellular Domains in the Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded BILF1 Receptor for Signaling and Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Downregulation.mBio. 2019 Jan 15;10(1):e01707-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01707-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30647152 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the constitutive activity and immunomodulatory properties of the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded G protein-coupled receptor BILF1.Immunity. 2021 Jul 13;54(7):1405-1416.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.06.001. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Immunity. 2021. PMID: 34216564 Free PMC article.
-
Sf9 cells: a versatile model system to investigate the pharmacological properties of G protein-coupled receptors.Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Dec;128(3):387-418. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.07.005. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20705094 Review.
-
Viral G protein-coupled receptors as modulators of cancer hallmarks.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Jun;156:104804. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104804. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32278040 Review.
Cited by
-
EBV BILF1 evolved to downregulate cell surface display of a wide range of HLA class I molecules through their cytoplasmic tail.J Immunol. 2013 Feb 15;190(4):1672-84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102462. Epub 2013 Jan 11. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23315076 Free PMC article.
-
Design and pharmacological characterization of VUF14480, a covalent partial agonist that interacts with cysteine 98(3.36) of the human histamine H₄ receptor.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep;170(1):89-100. doi: 10.1111/bph.12113. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23347159 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Significance of GPCR Heteromerization in the Neuro-Endocrine System.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2011 Feb 1;2:2. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2011.00002. eCollection 2011. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2011. PMID: 22649357 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Regulation of the Chemokine-Receptor Network.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Feb 7;18(2):342. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020342. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28178200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of TSPAN4 as Novel Histamine H4 Receptor Interactor.Biomolecules. 2021 Jul 30;11(8):1127. doi: 10.3390/biom11081127. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439793 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

