Reprogramming of human peripheral blood cells to induced pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 20621045
- PMCID: PMC2917234
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.06.002
Reprogramming of human peripheral blood cells to induced pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
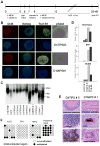
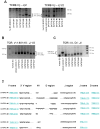
Direct reprogramming of human fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) has been achieved by ectopic expression of defined transcription factors. Derivation of human fibroblasts however is a time consuming process and requires punch biopsies or isolation of patient foreskin. Here we use a polycistronic vector encoding Oct4, Klf4, Sox2 and c-Myc to generate iPS cells from from frozen peripheral blood of several donors. Genomic DNA analyses indicated that iPS cells were derived from mature T cells as well as myeloid donor cells. Inducing pluripotency in peripheral blood would allow utilization of easy to get samples from the adult and, more importantly, provide convenient access to numerous patient samples stored in blood banks. The latter is of major interest as frozen blood samples, when reprogrammed to iPS cells, would allow the retrospective molecular analyses of rare diseases.
Figures
Comment in
-
Patient-specific pluripotent stem cells become even more accessible.Cell Stem Cell. 2010 Jul 2;7(1):1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.06.009. Cell Stem Cell. 2010. PMID: 20621038
Similar articles
-
Reprogramming of T cells from human peripheral blood.Cell Stem Cell. 2010 Jul 2;7(1):15-9. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.06.004. Cell Stem Cell. 2010. PMID: 20621044 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells (EURACi001-A, EURACi002-A, EURACi003-A) from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of three patients carrying mutations in the CAV3 gene.Stem Cell Res. 2018 Mar;27:25-29. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2017.12.012. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Stem Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 29304398
-
Episomal Reprogramming of Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells into Pluripotency.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2239:117-133. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1084-8_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33226616
-
Rapid and Efficient Generation of Transgene-Free iPSC from a Small Volume of Cryopreserved Blood.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015 Aug;11(4):652-65. doi: 10.1007/s12015-015-9586-8. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015. PMID: 25951995 Free PMC article.
-
[Expansion of MAIT cells via reprogramming to pluripotency and redifferentiation].Seikagaku. 2015 Feb;87(1):112-5. Seikagaku. 2015. PMID: 26571563 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The therapeutic potential of multiclonal tumoricidal T cells derived from tumor infiltrating lymphocyte-1derived iPS cells.Commun Biol. 2021 Jun 7;4(1):694. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02195-x. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34099861 Free PMC article.
-
The Generation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells from Blood Cells: An Efficient Protocol Using Serial Plating of Reprogrammed Cells by Centrifugation.Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:1329459. doi: 10.1155/2016/1329459. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Stem Cells Int. 2016. PMID: 27579041 Free PMC article.
-
iPSC-Derived Hepatocytes as a Platform for Disease Modeling and Drug Discovery.Front Med (Lausanne). 2019 Nov 15;6:265. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00265. eCollection 2019. Front Med (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31803747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promising Strategies for the Development of Advanced In Vitro Models with High Predictive Power in Ischaemic Stroke Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 27;23(13):7140. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137140. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human iPSC-Cardiomyocytes as an Experimental Model to Study Epigenetic Modifiers of Electrophysiology.Cells. 2022 Jan 7;11(2):200. doi: 10.3390/cells11020200. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35053315 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Davis MM, Bjorkman PJ. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature. 1988;334:395–402. - PubMed
-
- Evans MJ, Kaufman MH. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature. 1981;292:154–156. - PubMed
-
- Ferrante A, Thong YH. Optimal conditions for simultaneous purification of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leucocytes from human blood by the Hypaque-Ficoll method. Journal of immunological methods. 1980;36:109–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 CA087869-10/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HDO45022/PHS HHS/United States
- R01 HD045022-06/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA084198-12/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5-RO1-CA087869/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5-R37-CA084198/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HD045022/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA084198/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA087869/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD045022/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA084198/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

