NADPH oxidase 2 mediates intermittent hypoxia-induced mitochondrial complex I inhibition: relevance to blood pressure changes in rats
- PMID: 20618070
- PMCID: PMC3038125
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2010.3213
NADPH oxidase 2 mediates intermittent hypoxia-induced mitochondrial complex I inhibition: relevance to blood pressure changes in rats
Abstract
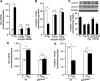
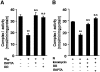
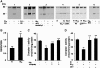
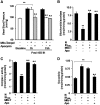
Previous studies identified NADPH oxidases (Nox) and mitochondrial electron transport chain at complex I as major cellular sources of reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediating systemic and cellular responses to intermittent hypoxia (IH). In the present study, we investigated potential interactions between Nox and the mitochondrial complex I and assessed the contribution of mitochondrial ROS in IH-evoked elevation in blood pressure. IH treatment led to stimulus-dependent activation of Nox and inhibition of complex I activity in rat pheochromocytoma (PC)12 cells. After re-oxygenation, Nox activity returned to baseline values within 3 h, whereas the complex I activity remained downregulated even after 24 h. IH-induced complex I inhibition was prevented by Nox inhibitors, Nox2 but not Nox 4 siRNA, in cell cultures and was absent in gp91(phox-/Y) (Nox2 knock-out; KO) mice. Using pharmacological inhibitors, we show that ROS generated by Nox activation mobilizes Ca(2+) flux from the cytosol to mitochondria, leading to S-glutathionylation of 75- and 50-kDa proteins of the complex I and inhibition of complex I activity, which results in elevated mitochondrial ROS. Systemic administration of mito-tempol prevented the sustained but not the acute elevations of blood pressure in IH-treated rats, suggesting that mitochondrial-derived ROS contribute to sustained elevation of blood pressure.
Figures
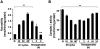
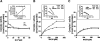
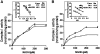
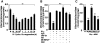
Similar articles
-
HIF-1α activation by intermittent hypoxia requires NADPH oxidase stimulation by xanthine oxidase.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 9;10(3):e0119762. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119762. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25751622 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 mediates increased expression of NADPH oxidase-2 in response to intermittent hypoxia.J Cell Physiol. 2011 Nov;226(11):2925-33. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22640. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21302291 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia activates NADPH oxidase to increase [ROS]i and [Ca2+]i through the mitochondrial ROS-PKCepsilon signaling axis in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2008 Nov 1;45(9):1223-31. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.06.012. Epub 2008 Jun 21. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008. PMID: 18638544 Free PMC article.
-
Sensory plasticity of the carotid body: role of reactive oxygen species and physiological significance.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011 Sep 30;178(3):375-80. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2011.05.012. Epub 2011 May 18. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21621009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross Talk Between Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species and Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Calcium in Pulmonary Arterial Smooth Muscle Cells.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;967:289-298. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-63245-2_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29047093 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between expression of NADPH oxidase 2 and invasion and prognosis of human gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 May 28;21(20):6271-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6271. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26034362 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress Response Kinetics after 60 Minutes at Different Levels (10% or 15%) of Normobaric Hypoxia Exposure.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 15;24(12):10188. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210188. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373334 Free PMC article.
-
Carotid body chemoreflex: a driver of autonomic abnormalities in sleep apnoea.Exp Physiol. 2016 Aug 1;101(8):975-85. doi: 10.1113/EP085624. Exp Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27474260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reactive oxygen species are involved in BMP-induced dendritic growth in cultured rat sympathetic neurons.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015 Jul;67:116-25. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2015.06.007. Epub 2015 Jun 14. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26079955 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α) heterozygous-null mice exhibit exaggerated carotid body sensitivity to hypoxia, breathing instability, and hypertension.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 15;108(7):3065-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1100064108. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21288809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bedard K. Krause KH. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:245–313. - PubMed
-
- Beer SM. Taylor ER. Brown SE. Dahm CC. Costa NJ. Runswick MJ. Murphy MP. Glutaredoxin 2 catalyzes the reversible oxidation and glutathionylation of mitochondrial membrane thiol proteins: implications for mitochondrial redox regulation and antioxidant defense. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:47939–47951. - PubMed
-
- Brandes RP. Triggering mitochondrial radical release: a new function for NADPH oxidases. Hypertension. 2005;45:847–848. - PubMed
-
- Daiber A. Redox signaling (cross-talk) from and to mitochondria involves mitochondrial pores and reactive oxygen species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1797:897–906. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

