Striatal microRNA controls cocaine intake through CREB signalling
- PMID: 20613834
- PMCID: PMC2916751
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09202
Striatal microRNA controls cocaine intake through CREB signalling
Abstract
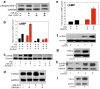
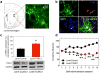
Cocaine addiction is characterized by a gradual loss of control over drug use, but the molecular mechanisms regulating vulnerability to this process remain unclear. Here we report that microRNA-212 (miR-212) is upregulated in the dorsal striatum of rats with a history of extended access to cocaine. Striatal miR-212 decreases responsiveness to the motivational properties of cocaine by markedly amplifying the stimulatory effects of the drug on cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) signalling. This action occurs through miR-212-enhanced Raf1 activity, resulting in adenylyl cyclase sensitization and increased expression of the essential CREB co-activator TORC (transducer of regulated CREB; also known as CRTC). Our findings indicate that striatal miR-212 signalling has a key role in determining vulnerability to cocaine addiction, reveal new molecular regulators that control the complex actions of cocaine in brain reward circuitries and provide an entirely new direction for the development of anti-addiction therapeutics based on the modulation of noncoding RNAs.
Figures
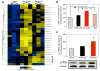
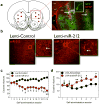
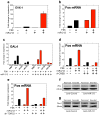
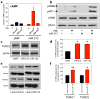
Comment in
-
Neuroscience: MicroRNA knocks down cocaine.Nature. 2010 Jul 8;466(7303):194-5. doi: 10.1038/466194a. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20613832 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Neuroscience: MicroRNA knocks down cocaine.Nature. 2010 Jul 8;466(7303):194-5. doi: 10.1038/466194a. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20613832 No abstract available.
-
Reflections on: "A general role for adaptations in G-Proteins and the cyclic AMP system in mediating the chronic actions of morphine and cocaine on neuronal function".Brain Res. 2016 Aug 15;1645:71-4. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.12.039. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26740398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antisense-induced reduction in nucleus accumbens cyclic AMP response element binding protein attenuates cocaine reinforcement.Neuroscience. 2006;137(2):373-83. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.10.049. Epub 2005 Dec 15. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16359811
-
A role for calmodulin-stimulated adenylyl cyclases in cocaine sensitization.J Neurosci. 2009 Feb 25;29(8):2393-403. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4356-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19244515 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular, cellular, and structural mechanisms of cocaine addiction: a key role for microRNAs.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Jan;38(1):198-211. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.120. Epub 2012 Sep 12. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 22968819 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of MicroRNA in Visceral Pain.J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015 Mar 30;21(2):159-71. doi: 10.5056/jnm15027. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015. PMID: 25843071 Free PMC article.
-
Associative and sensorimotor cortico-basal ganglia circuit roles in effects of abused drugs.Genes Brain Behav. 2017 Jan;16(1):71-85. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12309. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Genes Brain Behav. 2017. PMID: 27457495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Path to microRNA Therapeutics in Psychiatric and Neurodegenerative Disorders.Front Genet. 2012 May 17;3:82. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00082. eCollection 2012. Front Genet. 2012. PMID: 22629284 Free PMC article.
-
Prefrontal microRNA-221 Mediates Environmental Enrichment-Induced Increase of Locomotor Sensitivity to Nicotine.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015 Aug 1;19(1):pyv090. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyv090. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26232787 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation in opioid induced hyperalgesia.Neurobiol Pain. 2023 Nov 23;14:100146. doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2023.100146. eCollection 2023 Aug-Dec. Neurobiol Pain. 2023. PMID: 38099284 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McClung CA, Nestler EJ. Neuroplasticity mediated by altered gene expression. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008;33:3–17. - PubMed
-
- Kalivas PW, O’Brien CP. Drug addiction as a pathology of staged neuroplasticity. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008;33:166–180. - PubMed
-
- Carlezon WAJ, et al. Regulation of cocaine reward by CREB. Science. 1998;282:2272–2275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

