Organogenesis relies on SoxC transcription factors for the survival of neural and mesenchymal progenitors
- PMID: 20596238
- PMCID: PMC2892298
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms1008
Organogenesis relies on SoxC transcription factors for the survival of neural and mesenchymal progenitors
Abstract
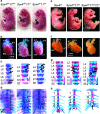
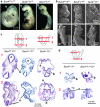
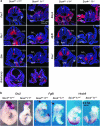
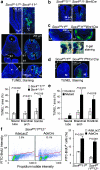
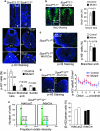
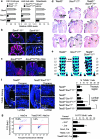
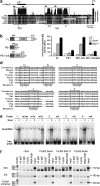
During organogenesis, neural and mesenchymal progenitor cells give rise to many cell lineages, but their molecular requirements for self-renewal and lineage decisions are incompletely understood. In this study, we show that their survival critically relies on the redundantly acting SoxC transcription factors Sox4, Sox11 and Sox12. The more SoxC alleles that are deleted in mouse embryos, the more severe and widespread organ hypoplasia is. SoxC triple-null embryos die at midgestation unturned and tiny, with normal patterning and lineage specification, but with massively dying neural and mesenchymal progenitor cells. Specific inactivation of SoxC genes in neural and mesenchymal cells leads to selective apoptosis of these cells, suggesting SoxC cell-autonomous roles. Tead2 functionally interacts with SoxC genes in embryonic development, and is a direct target of SoxC proteins. SoxC genes therefore ensure neural and mesenchymal progenitor cell survival, and function in part by activating this transcriptional mediator of the Hippo signalling pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The transcription factor protein Sox11 enhances early osteoblast differentiation by facilitating proliferation and the survival of mesenchymal and osteoblast progenitors.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 30;288(35):25400-25413. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.413377. Epub 2013 Jul 25. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23888050 Free PMC article.
-
Orchestration of Neuronal Differentiation and Progenitor Pool Expansion in the Developing Cortex by SoxC Genes.J Neurosci. 2015 Jul 22;35(29):10629-42. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1663-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26203155 Free PMC article.
-
SOXC are critical regulators of adult bone mass.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 5;15(1):2956. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47413-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38580651 Free PMC article.
-
Critical roles for SoxC transcription factors in development and cancer.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Mar;42(3):425-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.07.018. Epub 2009 Aug 3. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 19651233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SOXC Genes and the Control of Skeletogenesis.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2016 Feb;14(1):32-8. doi: 10.1007/s11914-016-0296-1. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2016. PMID: 26830765 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SOX4 cooperates with neurogenin 3 to regulate endocrine pancreas formation in mouse models.Diabetologia. 2015 May;58(5):1013-23. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3507-x. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Diabetologia. 2015. PMID: 25652387
-
SOX after SOX: SOXession regulates neurogenesis.Genes Dev. 2011 Dec 1;25(23):2423-8. doi: 10.1101/gad.181487.111. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 22156204 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and clinical factors associated with obesity among adult survivors of childhood cancer: A report from the St. Jude Lifetime Cohort.Cancer. 2015 Jul 1;121(13):2262-70. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29153. Epub 2015 May 11. Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25963547 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of SOX11 expression through CCND1 and STAT3 in mantle cell lymphoma.Blood. 2019 Jan 24;133(4):306-318. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-05-851667. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Blood. 2019. PMID: 30530749 Free PMC article.
-
SOX4 and RELA Function as Transcriptional Partners to Regulate the Expression of TNF- Responsive Genes in Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 22;13:789349. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.789349. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35529852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bernardo M. E., Locatelli F. & Fibbe W. E. Mesenchymal stromal cells. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1176, 101–117 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Kuhn N. Z. & Tuan R. S. Regulation of stemness and stem cell niche of mesenchymal stem cells: implications in tumorigenesis and metastasis. J. Cell. Physiol. 222, 268–277 (2010). - PubMed

