X-ray crystal structures of monomeric and dimeric peptide inhibitors in complex with the human neonatal Fc receptor, FcRn
- PMID: 20592032
- PMCID: PMC2934637
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.120667
X-ray crystal structures of monomeric and dimeric peptide inhibitors in complex with the human neonatal Fc receptor, FcRn
Abstract
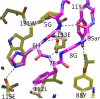
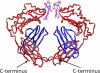
The neonatal Fc receptor, FcRn, is responsible for the long half-life of IgG molecules in vivo and is a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. A family of peptides comprising the consensus motif GHFGGXY, where X is preferably a hydrophobic amino acid, was shown previously to inhibit the human IgG:human FcRn protein-protein interaction (Mezo, A. R., McDonnell, K. A., Tan Hehir, C. A., Low, S. C., Palombella, V. J., Stattel, J. M., Kamphaus, G. D., Fraley, C., Zhang, Y., Dumont, J. A., and Bitonti, A. J. (2008) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 105, 2337-2342). Herein, the x-ray crystal structure of a representative monomeric peptide in complex with human FcRn was solved to 2.6 A resolution. The structure shows that the peptide binds to human FcRn at the same general binding site as does the Fc domain of IgG. The data correlate well with structure-activity relationship data relating to how the peptide family binds to human FcRn. In addition, the x-ray crystal structure of a representative dimeric peptide in complex with human FcRn shows how the bivalent ligand can bridge two FcRn molecules, which may be relevant to the mechanism by which the dimeric peptides inhibit FcRn and increase IgG catabolism in vivo. Modeling of the peptide:FcRn structure as compared with available structural data on Fc and FcRn suggest that the His-6 and Phe-7 (peptide) partially mimic the interaction of His-310 and Ile-253 (Fc) in binding to FcRn, but using a different backbone topology.
Figures


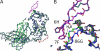
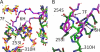
Similar articles
-
Structure-activity relationships of a peptide inhibitor of the human FcRn:human IgG interaction.Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Jun 15;16(12):6394-405. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.05.004. Epub 2008 May 6. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18501614
-
Crystal structure and immunoglobulin G binding properties of the human major histocompatibility complex-related Fc receptor(,).Biochemistry. 2000 Aug 15;39(32):9698-708. doi: 10.1021/bi000749m. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 10933786
-
Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of dimeric peptide antagonists of the human immunoglobulin G-human neonatal Fc receptor (IgG-FcRn) interaction.J Med Chem. 2010 Feb 25;53(4):1587-96. doi: 10.1021/jm901128z. J Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20092334
-
The multiple facets of FcRn in immunity.Immunol Rev. 2015 Nov;268(1):253-68. doi: 10.1111/imr.12331. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26497526 Review.
-
In Translation: FcRn across the Therapeutic Spectrum.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 17;22(6):3048. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063048. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33802650 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neonatal Fc receptor promotes immune complex-mediated glomerular disease.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 May;25(5):918-25. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013050498. Epub 2013 Dec 19. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24357670 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Interaction between FcRn and Albumin: Opportunities for Design of Albumin-Based Therapeutics.Front Immunol. 2015 Jan 26;5:682. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00682. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25674083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The immunologic functions of the neonatal Fc receptor for IgG.J Clin Immunol. 2013 Jan;33 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S9-17. doi: 10.1007/s10875-012-9768-y. Epub 2012 Sep 5. J Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 22948741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic FcRn regulates albumin homeostasis and susceptibility to liver injury.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Apr 4;114(14):E2862-E2871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1618291114. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28330995 Free PMC article.
-
The neonatal Fc receptor, FcRn, as a target for drug delivery and therapy.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015 Aug 30;91:109-24. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015. PMID: 25703189 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roopenian D. C., Akilesh S. (2007) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 7, 715–725 - PubMed
-
- Ghetie V., Ward E. S. (2000) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18, 739–766 - PubMed
-
- Andersen J. T., Sandlie I. (2009) Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 24, 318–332 - PubMed
-
- Roopenian D. C., Christianson G. J., Sproule T. J., Brown A. C., Akilesh S., Jung N., Petkova S., Avanessian L., Choi E. Y., Shaffer D. J., Eden P. A., Anderson C. L. (2003) J. Immunol. 170, 3528–3533 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

