JAK2 V617F constitutive activation requires JH2 residue F595: a pseudokinase domain target for specific inhibitors
- PMID: 20585391
- PMCID: PMC2886835
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011157
JAK2 V617F constitutive activation requires JH2 residue F595: a pseudokinase domain target for specific inhibitors
Abstract
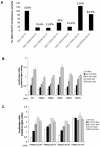
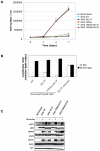
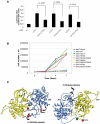
The JAK2 V617F mutation present in over 95% of Polycythemia Vera patients and in 50% of Essential Thrombocythemia and Primary Myelofibrosis patients renders the kinase constitutively active. In the absence of a three-dimensional structure for the full-length protein, the mechanism of activation of JAK2 V617F has remained elusive. In this study, we used functional mutagenesis to investigate the involvement of the JH2 alphaC helix in the constitutive activation of JAK2 V617F. We show that residue F595, located in the middle of the alphaC helix of JH2, is indispensable for the constitutive activity of JAK2 V617F. Mutation of F595 to Ala, Lys, Val or Ile significantly decreases the constitutive activity of JAK2 V617F, but F595W and F595Y are able to restore it, implying an aromaticity requirement at position 595. Substitution of F595 to Ala was also able to decrease the constitutive activity of two other JAK2 mutants, T875N and R683G, as well as JAK2 K539L, albeit to a lower extent. In contrast, the F595 mutants are activated by erythropoietin-bound EpoR. We also explored the relationship between the dimeric conformation of EpoR and several JAK2 mutants. Since residue F595 is crucial to the constitutive activation of JAK2 V617F but not to initiation of JAK2 activation by cytokines, we suggest that small molecules that target the region around this residue might specifically block oncogenic JAK2 and spare JAK2 wild-type.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Janus kinase 2 activation mechanisms revealed by analysis of suppressing mutations.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Apr;143(4):1549-1559.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.07.022. Epub 2018 Aug 6. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30092288 Free PMC article.
-
Uncoupling JAK2 V617F activation from cytokine-induced signalling by modulation of JH2 αC helix.Biochem J. 2016 Jun 1;473(11):1579-91. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160085. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 27029346 Free PMC article.
-
The constitutive activation of Jak2-V617F is mediated by a π stacking mechanism involving phenylalanines 595 and 617.Biochemistry. 2010 Nov 23;49(46):9972-84. doi: 10.1021/bi1014858. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20958061 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the structure and function of the pseudokinase domain in JAK2.Biochem Soc Trans. 2013 Aug;41(4):1002-7. doi: 10.1042/BST20130005. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013. PMID: 23863170 Review.
-
Insights into the Structural Features Essential for JAK2 Inhibition and Selectivity.Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(13):1331-55. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666160405112615. Curr Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27048338 Review.
Cited by
-
Janus kinase deregulation in leukemia and lymphoma.Immunity. 2012 Apr 20;36(4):529-41. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.03.017. Immunity. 2012. PMID: 22520846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of activation-loop phosphorylation by JAK inhibitors is binding mode dependent.Cancer Discov. 2012 Jun;2(6):512-523. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0324. Epub 2012 May 3. Cancer Discov. 2012. PMID: 22684457 Free PMC article.
-
JAK2 inhibitors: are they the solution?Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2011 Jun;11 Suppl 1(0 1):S28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2011.02.007. Epub 2011 May 4. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2011. PMID: 22035745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of a pseudokinase-domain switch that controls oncogenic activation of Jak kinases.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013 Oct;20(10):1221-3. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2673. Epub 2013 Sep 8. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24013208 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of the JAK2 pseudokinase domain and the pathogenic mutant V617F.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Aug;19(8):754-9. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2348. Epub 2012 Jul 22. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22820988 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ziemiecki A, Harpur AG, Wilks AF. JAK protein tyrosine kinases: their role in cytokine signalling. Trends Cell Biol. 1994;4:207–212. - PubMed
-
- Huang LJ, Constantinescu SN, Lodish HF. The N-terminal domain of Janus kinase 2 is required for Golgi processing and cell surface expression of erythropoietin receptor. Mol Cell. 2001;8:1327–1338. - PubMed
-
- Radtke S, Hermanns HM, Haan C, Schmitz-Van De Leur H, Gascan H, et al. Novel role of Janus kinase 1 in the regulation of oncostatin M receptor surface expression. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:11297–11305. - PubMed
-
- Royer Y, Staerk J, Costuleanu M, Courtoy PJ, Constantinescu SN. Janus kinases affect thrombopoietin receptor cell surface localization and stability. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:27251–27261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

