A small ubiquitin-related modifier-interacting motif functions as the transcriptional activation domain of Krüppel-like factor 4
- PMID: 20584900
- PMCID: PMC2934694
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.101717
A small ubiquitin-related modifier-interacting motif functions as the transcriptional activation domain of Krüppel-like factor 4
Abstract
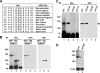
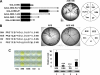
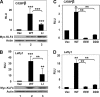
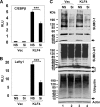
The zinc finger transcription factor, Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4), regulates numerous biological processes, including proliferation, differentiation, and embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Although the DNA sequence to which KLF4 binds is established, the mechanism by which KLF4 controls transcription is not well defined. Small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) is an important regulator of transcription. Here we show that KLF4 is both SUMOylated at a single lysine residue and physically interacts with SUMO-1 in a region that matches an acidic and hydrophobic residue-rich SUMO-interacting motif (SIM) consensus. The SIM in KLF4 is required for transactivation of target promoters in a SUMO-1-dependent manner. Mutation of either the acidic or hydrophobic residues in the SIM significantly impairs the ability of KLF4 to interact with SUMO-1, activate transcription, and inhibit cell proliferation. Our study provides direct evidence that SIM in KLF4 functions as a transcriptional activation domain. A survey of transcription factor sequences reveals that established transactivation domains of many transcription factors contain sequences highly related to SIM. These results, therefore, illustrate a novel mechanism by which SUMO interaction modulates the activity of transcription factors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Kruppel zinc finger of ZNF 146 interacts with the SUMO-1 conjugating enzyme UBC9 and is sumoylated in vivo.Mol Cell Biochem. 2005 Mar;271(1-2):215-23. doi: 10.1007/s11010-005-6417-2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15881673
-
The role of small ubiquitin-like modifier-interacting motif in the assembly and regulation of metal-responsive transcription factor 1.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 16;286(50):42818-29. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.253203. Epub 2011 Oct 22. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22021037 Free PMC article.
-
Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) modification of zinc finger protein 131 potentiates its negative effect on estrogen signaling.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 18;287(21):17517-17529. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.336354. Epub 2012 Mar 30. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22467880 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO Interacting Motifs: Structure and Function.Cells. 2021 Oct 21;10(11):2825. doi: 10.3390/cells10112825. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of SUMO-binding motifs by NMR.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;497:121-38. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-566-4_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19107414 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Krüppel-like factor 4 regulates genetic stability in mouse embryonic fibroblasts.Mol Cancer. 2013 Aug 6;12:89. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-89. Mol Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23919723 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insight into KLF4 proteolytic regulation in estrogen receptor signaling and breast carcinogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 20;287(17):13584-97. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.343566. Epub 2012 Mar 2. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22389506 Free PMC article.
-
MBNL2 promotes aging-related cardiac fibrosis via inhibited SUMOylation of Krüppel-like factor4.iScience. 2024 Jun 3;27(7):110163. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110163. eCollection 2024 Jul 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38974966 Free PMC article.
-
The post-translational modification, SUMOylation, and cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2018 Apr;52(4):1081-1094. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4280. Epub 2018 Feb 22. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29484374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Krüppel-like Factors 4 and 5 in Colorectal Tumorigenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 24;15(9):2430. doi: 10.3390/cancers15092430. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37173904 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Triezenberg S. J. (1995) Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 5, 190–196 - PubMed
-
- Chang J., Kim D. H., Lee S. W., Choi K. Y., Sung Y. C. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270, 25014–25019 - PubMed
-
- Seipel K., Georgiev O., Schaffner W. (1994) Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 375, 463–470 - PubMed
-
- Sekiyama N., Ikegami T., Yamane T., Ikeguchi M., Uchimura Y., Baba D., Ariyoshi M., Tochio H., Saitoh H., Shirakawa M. (2008) J. Biol. Chem. 283, 35966–35975 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K01 DK076742-05/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK089131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK052230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK052230-13S2/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK052230-14/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK64399/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK077381-03/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK064399/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK076742/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK52230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA084197-12/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK089131-02/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA84197/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK77381/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK077381/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK76742/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK052230-13/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA084197/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK064399-09/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK064399-08/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA084197-13/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

