Structural basis for the suppression of skin cancers by DNA polymerase eta
- PMID: 20577207
- PMCID: PMC3030469
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09104
Structural basis for the suppression of skin cancers by DNA polymerase eta
Abstract
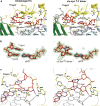
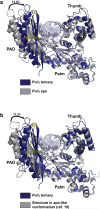
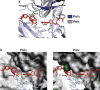
DNA polymerase eta (Poleta) is unique among eukaryotic polymerases in its proficient ability for error-free replication through ultraviolet-induced cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers, and inactivation of Poleta (also known as POLH) in humans causes the variant form of xeroderma pigmentosum (XPV). We present the crystal structures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Poleta (also known as RAD30) in ternary complex with a cis-syn thymine-thymine (T-T) dimer and with undamaged DNA. The structures reveal that the ability of Poleta to replicate efficiently through the ultraviolet-induced lesion derives from a simple and yet elegant mechanism, wherein the two Ts of the T-T dimer are accommodated in an active site cleft that is much more open than in other polymerases. We also show by structural, biochemical and genetic analysis that the two Ts are maintained in a stable configuration in the active site via interactions with Gln 55, Arg 73 and Met 74. Together, these features define the basis for Poleta's action on ultraviolet-damaged DNA that is crucial in suppressing the mutagenic and carcinogenic consequences of sun exposure, thereby reducing the incidence of skin cancers in humans.
Figures
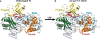
Comment in
-
DNA repair: How to accurately bypass damage.Nature. 2010 Jun 24;465(7301):1023-4. doi: 10.1038/4651023a. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20577203 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Structure and mechanism of human DNA polymerase eta.Nature. 2010 Jun 24;465(7301):1044-8. doi: 10.1038/nature09196. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20577208 Free PMC article.
-
DNA repair: How to accurately bypass damage.Nature. 2010 Jun 24;465(7301):1023-4. doi: 10.1038/4651023a. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20577203 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient bypass of a thymine-thymine dimer by yeast DNA polymerase, Poleta.Science. 1999 Feb 12;283(5404):1001-4. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5404.1001. Science. 1999. PMID: 9974380
-
Replication of damaged DNA: molecular defect in xeroderma pigmentosum variant cells.Mutat Res. 1999 Oct 22;435(2):111-9. doi: 10.1016/s0921-8777(99)00047-6. Mutat Res. 1999. PMID: 10556591 Review.
-
The RAD30 cancer susceptibility gene.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Feb;31(Pt 1):252-6. doi: 10.1042/bst0310252. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 12546696 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural mechanism of replication stalling on a bulky amino-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon DNA adduct by a y family DNA polymerase.J Mol Biol. 2013 Nov 15;425(22):4167-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.07.020. Epub 2013 Jul 20. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23876706 Free PMC article.
-
The Translesion Polymerase Pol η Is Required for Efficient Epstein-Barr Virus Infectivity and Is Regulated by the Viral Deubiquitinating Enzyme BPLF1.J Virol. 2017 Sep 12;91(19):e00600-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00600-17. Print 2017 Oct 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28724765 Free PMC article.
-
The structure and duplex context of DNA interstrand crosslinks affects the activity of DNA polymerase η.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 6;44(15):7281-91. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw485. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27257072 Free PMC article.
-
Human DNA polymerase η is pre-aligned for dNTP binding and catalysis.J Mol Biol. 2012 Jan 27;415(4):627-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.11.038. Epub 2011 Nov 29. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22154937 Free PMC article.
-
Y-family polymerase conformation is a major determinant of fidelity and translesion specificity.Structure. 2013 Jan 8;21(1):20-31. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.11.005. Epub 2012 Dec 13. Structure. 2013. PMID: 23245850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnson RE, Kondratick CM, Prakash S, Prakash L. hRAD30 mutations in the variant form of xeroderma pigmentosum. Science. 1999;285:263–5. see comments. - PubMed
-
- Masutani C, et al. The XPV (xeroderma pigmentosum variant) gene encodes human DNA polymerase eta. Nature. 1999;399:700–4. see comments. - PubMed
-
- Gratchev A, Strein P, Utikal J, Sergij G. Molecular genetics of Xeroderma pigmentosum variant. Exp Dermatol. 2003;12:529–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

