Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 regulates matrix metalloproteinase-2-mediated endothelial barrier dysfunction and breast cancer cell transmigration through lung microvascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 20571065
- PMCID: PMC5584073
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0523
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 regulates matrix metalloproteinase-2-mediated endothelial barrier dysfunction and breast cancer cell transmigration through lung microvascular endothelial cells
Abstract
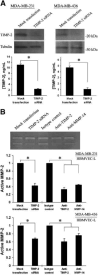
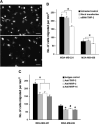
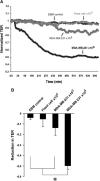
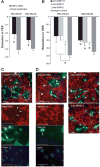
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) have been implicated in multiple stages of cancer metastasis. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2) plays an important role in regulating MMP-2 activity. By forming a ternary complex with pro-MMP-2 and its activator MMP-14 on the cell surface, TIMP-2 can either initiate or restrain the cleavage and subsequent activation of MMP-2. Our recent work has shown that breast cancer cell adhesion to vascular endothelial cells activates endothelial MMP-2, promoting tumor cell transendothelial migration (TEM(E)). However, the mechanism of MMP-2 regulation during TEM(E) remains unclear. In the current study, we present evidence that MMP-14 is expressed in both invasive breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-436) and lung microvascular endothelial cells (HBMVEC-L), whereas TIMP-2 is exclusively expressed and released from the cancer cells. The tumor cell-derived TIMP-2 was further identified as a major determinant of endothelial MMP-2 activity during tumor cell transmigration in the presence of MMP-14. This response was associated with endothelial barrier dysfunction because coculture of MDA-MB-231 or MDA-MB-436 with HBMVEC-L caused a significant decrease in transendothelial electrical resistance concomitantly with endothelial cell-cell junction disruption and tumor cell transmigration. Knockdown of TIMP-2 or inhibition of TIMP-2/MMP-14 attenuated MMP-2-dependent transendothelial electrical resistance response and TEM(E). These findings suggest a novel interactive role of breast cancer cells and vascular endothelial cells in regulating the TIMP-2/MMP-14/MMP-2 pathway during tumor metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Far Posterior Approach for Rib Fracture Fixation: Surgical Technique and Tips.JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2024 Dec 6;14(4):e23.00094. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.ST.23.00094. eCollection 2024 Oct-Dec. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2024. PMID: 39650795 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered TIMP2 with narrow MMP-9 specificity is an effective inhibitor of invasion and proliferation of triple-negative breast cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2024 Nov;300(11):107867. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107867. Epub 2024 Oct 15. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39419285 Free PMC article.
-
Can a Liquid Biopsy Detect Circulating Tumor DNA With Low-passage Whole-genome Sequencing in Patients With a Sarcoma? A Pilot Evaluation.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jan 1;483(1):39-48. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003161. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 38905450
-
Trends in Surgical and Nonsurgical Aesthetic Procedures: A 14-Year Analysis of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery-ISAPS.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(20):4217-4227. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04260-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39103642 Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor induces vascular leakage via autophagy.Biol Open. 2015 Jan 23;4(2):244-52. doi: 10.1242/bio.201410322. Biol Open. 2015. PMID: 25617421 Free PMC article.
-
CD147 functions as the signaling receptor for extracellular divalent copper in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Oncotarget. 2017 May 9;8(31):51151-51163. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17712. eCollection 2017 Aug 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28881637 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of elastin-derived peptides on the production of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1, -2, and -3 and the ratios in various endothelial cell lines.Exp Ther Med. 2015 Jun;9(6):2245-2250. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2429. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Exp Ther Med. 2015. PMID: 26136968 Free PMC article.
-
The SEMA3F-NRP1/NRP2 axis is a key factor in the acquisition of invasive traits in in situ breast ductal carcinoma.Breast Cancer Res. 2024 Aug 13;26(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s13058-024-01871-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39138514 Free PMC article.
-
DCBLD1 is associated with the integrin signaling pathway and has prognostic value in non-small cell lung and invasive breast carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 17;11(1):12753. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92090-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34140574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kamby C, Ejlertsen B, Andersen J, et al. The pattern of metastases in human breast cancer. Influence of systemic adjuvant therapy and impact on survival. Acta Oncol. 1988;27:715–9. - PubMed
-
- Patanaphan V, Salazar OM, Risco R. Breast cancer: metastatic patterns and their prognosis. South Med J. 1988;81:1109–12. - PubMed
-
- Murphy G, Stanton H, Cowell S, et al. Mechanisms for pro matrix metalloproteinase activation. Apmis. 1999;107:38–44. - PubMed
-
- Ellerbroek SM, Stack MS. Membrane associated matrix metalloproteinases in metastasis. Bioessays. 1999;21:940–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

