Cooperative signaling between Wnt1 and integrin-linked kinase induces accelerated breast tumor development
- PMID: 20565980
- PMCID: PMC2917033
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2592
Cooperative signaling between Wnt1 and integrin-linked kinase induces accelerated breast tumor development
Abstract
Introduction: Breast cancer is genetically and clinically a heterogeneous disease. However, the exact contribution of different cell types and oncogenic mutations to this heterogeneity are not well understood. Recently, we discovered an interaction between Wnt and integrin-linked kinase (ILK) within the signaling cascade that regulates cell growth and survival. Interestingly, mammary-specific expression of either one of these proteins has been shown to promote mammary tumorigenesis. In light of our recent findings and to investigate the potential interaction between Wnt and ILK proteins during mammary tumor formation and progression, we established a transgenic mouse model that expresses both Wnt and ILK in mammary epithelial cells.
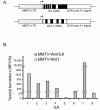
Methods: A novel transgenic mouse model with mammary-specific expression of both Wnt1 and ILK was generated by crossing the two previously characterized mouse models, MMTV-Wnt1 and MMTV-ILK. The resulting MMTV-Wnt/ILK mice were closely monitored for tumor development and growth, as well as for the tumor onset. The molecular phenotypes of both tumors and premalignant mammary glands were investigated by using biochemical and global gene-expression analysis approaches.
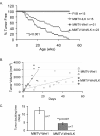
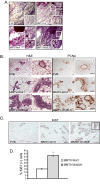
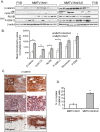
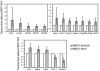
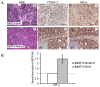
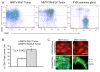
Results: A significant acceleration in mammary tumor incidence and growth was observed in the MMTV-Wnt/ILK mice. Pre-neoplastic mammary glands also display lobuloalveolar hyperplasia and an increase in ductal epithelium proliferation. Apart from elevated expression of Wnt/ILK targets, such as beta-catenin and cyclin D1, gene-expression profiling identified the surprising activation of the FOXA1 transcription factor. Upregulation of FOXA1, which is also known as the molecular marker of differentiated mammary luminal cells, was consistent with the expansion of the enriched luminal progenitor population or CD29loCD24hiCD61+ cells in MMTV-Wnt/ILK tumors.
Conclusions: These results show cooperation between Wnt1 and ILK transgenes during mammary carcinogenesis, leading to changes in a transcriptional network, which could dictate a specific breast cancer phenotype with enhanced growth dynamics. The MMTV-Wnt/ILK can be used as a model to identify further the genes downstream of the estrogen receptor-beta/FOXA1 and to investigate the mechanisms targeting the expansion of the luminal progenitor cells leading to hyperplasia and tumorigenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wnt5a suppresses tumor formation and redirects tumor phenotype in MMTV-Wnt1 tumors.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 17;9(11):e113247. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113247. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25401739 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling dramatically accelerates tumorigenesis and enhances oncoprotein translation in the mouse mammary tumor virus-Wnt-1 mouse model of breast cancer.Cancer Res. 2010 Jun 15;70(12):4868-79. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4404. Epub 2010 May 25. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20501844 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy regulator BECN1 suppresses mammary tumorigenesis driven by WNT1 activation and following parity.Autophagy. 2014;10(11):2036-52. doi: 10.4161/auto.34398. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Autophagy. 2014. PMID: 25483966 Free PMC article.
-
MMTV mouse models and the diagnostic values of MMTV-like sequences in human breast cancer.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2009 Jul;9(5):423-40. doi: 10.1586/erm.09.31. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2009. PMID: 19580428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt signaling, stem cells, and the cellular origin of breast cancer.Stem Cell Rev. 2007 Jun;3(2):157-68. doi: 10.1007/s12015-007-0025-3. Stem Cell Rev. 2007. PMID: 17873348 Review.
Cited by
-
Deletion of tetraspanin CD151 alters the Wnt oncogene-induced mammary tumorigenesis: A cell type-linked function and signaling.Neoplasia. 2019 Dec;21(12):1151-1163. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2019.08.005. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Neoplasia. 2019. PMID: 31783316 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin-linked kinase regulates p38 MAPK-dependent cell cycle arrest in ureteric bud development.Development. 2010 Oct;137(19):3233-43. doi: 10.1242/dev.052845. Development. 2010. PMID: 20823064 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Analysis Reveals the Gut Microbial Metabolite TMAO Promotes Inflammatory Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Upregulating POSTN.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 May 23;10:840171. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.840171. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35676936 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) in tumorigenesis and its potential implication as a biomarker and therapeutic target for human cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 1;9(1):186-197. eCollection 2019. Am J Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30755822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crossroads of integrins and cadherins in epithelia and stroma remodeling.Cell Adh Migr. 2012 May-Jun;6(3):261-73. doi: 10.4161/cam.20253. Epub 2012 May 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2012. PMID: 22568988 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Veeck J, Niederacher D, An H, Klopocki E, Wiesmann F, Betz B, Galm O, Camara O, Durst M, Kristiansen G, Huszka C, Knuchel R, Dahl E. Aberrant methylation of the Wnt antagonist SFRP1 in breast cancer is associated with unfavourable prognosis. Oncogene. 2006;25:3479–3488. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209386. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

