Effect of pseudouridylation on the structure and activity of the catalytically essential P6.1 hairpin in human telomerase RNA
- PMID: 20554853
- PMCID: PMC2965242
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq525
Effect of pseudouridylation on the structure and activity of the catalytically essential P6.1 hairpin in human telomerase RNA
Abstract
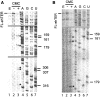
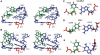
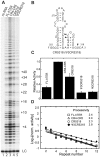
Telomerase extends the 3'-ends of linear chromosomes by adding conserved telomeric DNA repeats and is essential for cell proliferation and genomic stability. Telomerases from all organisms contain a telomerase reverse transcriptase and a telomerase RNA (TER), which together provide the minimal functional elements for catalytic activity in vitro. The RNA component of many functional ribonucleoproteins contains modified nucleotides, including conserved pseudouridines (Ψs) that can have subtle effects on structure and activity. We have identified potential Ψ modification sites in human TER. Two of the predicted Ψs are located in the loop of the essential P6.1 hairpin from the CR4-CR5 domain that is critical for telomerase catalytic activity. We investigated the effect of P6.1 pseudouridylation on its solution NMR structure, thermodynamic stability of folding and telomerase activation in vitro. The pseudouridylated P6.1 has a significantly different loop structure and increase in stability compared to the unmodified P6.1. The extent of loop nucleotide interaction with adjacent residues more closely parallels the extent of loop nucleotide evolutionary sequence conservation in the Ψ-modified P6.1 structure. Pseudouridine-modification of P6.1 slightly attenuates telomerase activity but slightly increases processivity in vitro. Our results suggest that Ψs could have a subtle influence on human telomerase activity via impact on TER-TERT or TER-TER interactions.
Figures


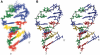
Similar articles
-
A critical stem-loop structure in the CR4-CR5 domain of mammalian telomerase RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 15;30(2):592-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.2.592. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 11788723 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and sequence elements of the CR4/5 domain of medaka telomerase RNA important for telomerase function.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Mar;42(5):3395-408. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1276. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24335084 Free PMC article.
-
The structure of an enzyme-activating fragment of human telomerase RNA.RNA. 2005 Apr;11(4):394-403. doi: 10.1261/rna.7222505. Epub 2005 Feb 9. RNA. 2005. PMID: 15703438 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of telomerase RNA.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006 Jun;16(3):307-18. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2006.05.005. Epub 2006 May 18. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006. PMID: 16713250 Review.
-
Structural Biology of Telomerase.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019 Dec 2;11(12):a032383. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a032383. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019. PMID: 31451513 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the pathogenesis of Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson syndrome, a complex telomere biology disorder.Br J Haematol. 2015 Aug;170(4):457-71. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13442. Epub 2015 May 4. Br J Haematol. 2015. PMID: 25940403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of human telomerase assembly inhibitors enabled by a novel method to produce hTERT.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Sep 3;43(15):e99. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv425. Epub 2015 May 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25958399 Free PMC article.
-
Computational and NMR studies of RNA duplexes with an internal pseudouridine-adenosine base pair.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 7;9(1):16278. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52637-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31700156 Free PMC article.
-
Telomere Maintenance and the cGAS-STING Pathway in Cancer.Cells. 2022 Jun 17;11(12):1958. doi: 10.3390/cells11121958. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35741087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telomerase regulation.Mutat Res. 2012 Feb 1;730(1-2):20-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2011.10.003. Epub 2011 Oct 18. Mutat Res. 2012. PMID: 22032831 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cohn WE. Pseudouridine, a carbon-carbon linked ribonucleoside in ribonucleic acids: isolation, structure, and chemical characteristics. J. Biol. Chem. 1960;235:1488–1498. - PubMed
-
- Hamma T, Ferre-D’Amare AR. Pseudouridine synthases. Chem. Biol. 2006;13:1125–1135. - PubMed
-
- Charette M, Gray MW. Pseudouridine in RNA: what, where, how, and why. IUBMB Life. 2000;49:341–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions

