Distinctive structure and interfacial activity of the human apolipoprotein A-IV 347S isoprotein
- PMID: 20554794
- PMCID: PMC2918448
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M007021
Distinctive structure and interfacial activity of the human apolipoprotein A-IV 347S isoprotein
Abstract
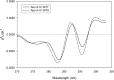
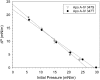
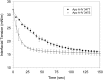
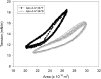
The T347S polymorphism in the human apolipoprotein (apo) A-IV gene is present at high frequencies among all the world's populations. Carriers of a 347S allele exhibit faster clearance of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, greater adiposity, and increased risk for developing atherosclerosis, which suggests that this conservative amino acid substitution alters the structure of apo A-IV. Herein we have used spectroscopic and surface chemistry techniques to examine the structure, stability, and interfacial properties of the apo A-IV 347S isoprotein. Circular dichroism spectroscopy revealed that the 347S isoprotein has similar alpha-helical structure but lower thermodynamic stability than the 347T isoprotein. Fluorescence spectroscopy found that the 347S isoprotein exhibits an enhanced tyrosine emission and reduced tyrosine-->tryptophan energy transfer, and second derivative UV absorption spectra noted increased tyrosine exposure, suggesting that the 347S isoprotein adopts a looser tertiary conformation. Surface chemistry studies found that although the 347S isoprotein bound rapidly to the lipid interface, it has a lower interfacial exclusion pressure and lower elastic modulus than the 347T isoprotein. Together, these observations establish that the T347S substitution alters the conformation of apo A-IV and lowers its interfacial activity-changes that could account for the effect of this polymorphism on postprandial lipid metabolism.
Figures
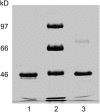
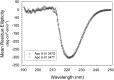
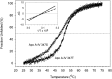
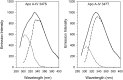
Similar articles
-
Interfacial exclusion pressure determines the ability of apolipoprotein A-IV truncation mutants to activate cholesterol ester transfer protein.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jun 14;277(24):21549-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M202197200. Epub 2002 Apr 8. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11940599
-
Apolipoprotein A-IV polymorphisms and diet-gene interactions.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2002 Apr;13(2):125-34. doi: 10.1097/00041433-200204000-00003. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2002. PMID: 11891414 Review.
-
Effect of the apolipoprotein A-IV Q360H polymorphism on postprandial plasma triglyceride clearance.J Lipid Res. 2001 Feb;42(2):211-7. J Lipid Res. 2001. PMID: 11181750
-
Effects of phospholipid on the structure of human apolipoprotein A-IV.J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8081-6. J Biol Chem. 1990. PMID: 2335517
-
Apolipoprotein(a): structure-function relationship at the lysine-binding site and plasminogen activator cleavage site.Biol Chem. 2002 Jan;383(1):93-9. doi: 10.1515/BC.2002.009. Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11928826 Review.
References
-
- Mann C. J., Anderson T. A., Read J., Chester S. A., Harrison G. B., Kochl S., Ritchie P. J., Bradbury P., Hussain F. S., Amey J., et al. 1999. The structure of vitellogenin provides a molecular model for the assembly and secretion of atherogenic lipoproteins. J. Mol. Biol. 285: 391–408. - PubMed
-
- Luo C. C., Li W. H., Moore M. N., Chan L. 1986. Structure and evolution of the apolipoprotein multigene family. J. Mol. Biol. 187: 325–340. - PubMed
-
- Weinberg R. B., Scanu A. M. 1983. The isolation and characterization of human apolipoprotein A-IV from lipoprotein depleted serum. J. Lipid Res. 24: 52–59. - PubMed
-
- Kalogeris T. J., Rodriquez M. D., Tso P. 1997. Control of synthesis and secretion of intestinal apolipoprotein A-IV. J. Nutr. 127: 537S–543S. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi H., Nutting D. F., Fujimoto K., Cardelli J. A., Black D., Tso P. 1990. Transport of lipid and apolipoproteins apo A-I and apo A-IV in intestinal lymph of the rat. J. Lipid Res. 31: 1613–1625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

