Mammary gland growth factors: roles in normal development and in cancer
- PMID: 20554705
- PMCID: PMC2908768
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003186
Mammary gland growth factors: roles in normal development and in cancer
Abstract
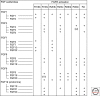
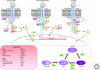
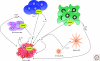
Normal development of the mammary gland proceeds via interactions between the epithelium and the mesenchyme that start during embryogenesis and continue during pubertal outgrowth and differentiation. The function of specific peptide growth factors that bind members of the receptor tyrosine kinase family and the cytokine receptor family are required at each stage. In many cases the peptides are produced in one compartment and act on receptors in the other compartment. One of the striking differences between normal development and cancer is the loss of this cross-talk. Mammary tumor cells often produce a peptide and express the receptor on the same cell leading to autocrine activation of signaling pathways, a mechanism that is characteristic for cancer cells. We will discuss different peptides in the context of normal development and cancer in this review.
Figures
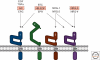

Similar articles
-
Cadherins and the mammary gland.J Cell Biochem. 2005 Jun 1;95(3):488-96. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20419. J Cell Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15838893 Review.
-
NF-kappaB in mammary gland development and breast cancer.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2003 Apr;8(2):215-23. doi: 10.1023/a:1025905008934. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2003. PMID: 14635796 Review.
-
Key signaling nodes in mammary gland development and cancer: β-catenin.Breast Cancer Res. 2010;12(6):213. doi: 10.1186/bcr2723. Epub 2010 Nov 3. Breast Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21067528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of NRG3 in mammary development.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008 Jun;13(2):195-203. doi: 10.1007/s10911-008-9082-8. Epub 2008 Apr 17. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008. PMID: 18418701 Review.
-
Constitutive activation of JAK2 in mammary epithelium elevates Stat5 signalling, promotes alveologenesis and resistance to cell death, and contributes to tumourigenesis.Cell Death Differ. 2012 Mar;19(3):511-22. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.122. Epub 2011 Sep 23. Cell Death Differ. 2012. PMID: 21941370 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Defining and targeting macrophage heterogeneity in the mammary gland and breast cancer.Cancer Med. 2024 Feb;13(3):e7053. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7053. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38426622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MUC1 triggers lineage plasticity of Her2 positive mammary tumors.Oncogene. 2022 May;41(22):3064-3078. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02320-y. Epub 2022 Apr 23. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 35461328
-
Modulation of fibroblast growth factor signaling is essential for mammary epithelial morphogenesis.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 9;9(4):e92735. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092735. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24718286 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin-associated CD151 drives ErbB2-evoked mammary tumor onset and metastasis.Neoplasia. 2012 Aug;14(8):678-89. doi: 10.1593/neo.12922. Neoplasia. 2012. PMID: 22952421 Free PMC article.
-
High levels of dietary soy decrease mammary tumor latency and increase incidence in MTB-IGFIR transgenic mice.BMC Cancer. 2015 Feb 6;15:37. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1037-z. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25655427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adnane J, Gaudray P, Dionne CA, Crumley G, Jaye M, Schlessinger J, Jeanteur P, Birnbaum D, Theillet C 1991. BEK and FLG, two receptors to members of the FGF family, are amplified in subsets of human breast cancers. Oncogene 6: 659–663 - PubMed
-
- Anderson E, Clarke RB 2004. Steroid receptors and cell cycle in normal mammary epithelium. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 9: 3–13 - PubMed
-
- Andrechek ER, White D, Muller WJ 2005. Targeted disruption of ErbB2/Neu in the mammary epithelium results in impaired ductal outgrowth. Oncogene 24: 932–937 - PubMed
-
- Asselin-Labat ML, Sutherland KD, Barker H, Thomas R, Shackleton M, Forrest NC, Hartley L, Robb L, Grosveld FG, van der Wees J, et al.2007. Gata-3 is an essential regulator of mammary-gland morphogenesis and luminal-cell differentiation. Nat Cell Biol 9: 201–209 - PubMed
-
- Bange J, Prechtl D, Cheburkin Y, Specht K, Harbeck N, Schmitt M, Knyazeva T, Muller S, Gartner S, Sures I, et al.2002. Cancer progression and tumor cell motility are associated with the FGFR4 Arg(388) allele. Cancer Res 62: 840–847 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
