Overcoming cancer cell resistance to Smac mimetic induced apoptosis by modulating cIAP-2 expression
- PMID: 20547836
- PMCID: PMC2900705
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1005667107
Overcoming cancer cell resistance to Smac mimetic induced apoptosis by modulating cIAP-2 expression
Abstract
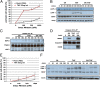
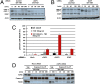
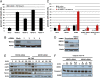
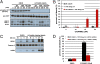
Smac mimetics target cancer cells in a TNFalpha-dependent manner, partly via proteasome degradation of cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1 (cIAP1) and cIAP2. Degradation of cIAPs triggers the release of receptor interacting protein kinase (RIPK1) from TNF receptor I (TNFR1) to form a caspase-8 activating complex together with the adaptor protein Fas-associated death domain (FADD). We report here a means through which cancer cells mediate resistance to Smac mimetic/TNFalpha-induced apoptosis and corresponding strategies to overcome such resistance. These human cancer cell lines evades Smac mimetic-induced apoptosis by up-regulation of cIAP2, which although initially degraded, rebounds and is refractory to subsequent degradation. cIAP2 is induced by TNFalpha via NF-kappaB and modulation of the NF-kappaB signal renders otherwise resistant cells sensitive to Smac mimetics. In addition, other signaling pathways, including phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase (PI3K), have the potential to concurrently regulate cIAP2. Using the PI3K inhibitor, LY294002, cIAP2 up-regulation was suppressed and resistance to Smac mimetics-induced apoptosis was also overcome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular determinants of Smac mimetic induced degradation of cIAP1 and cIAP2.Cell Death Differ. 2011 Aug;18(8):1376-86. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.10. Epub 2011 Feb 18. Cell Death Differ. 2011. PMID: 21331077 Free PMC article.
-
Smac mimetic bypasses apoptosis resistance in FADD- or caspase-8-deficient cells by priming for tumor necrosis factor α-induced necroptosis.Neoplasia. 2011 Oct;13(10):971-9. doi: 10.1593/neo.11610. Neoplasia. 2011. PMID: 22028622 Free PMC article.
-
CLL cells are resistant to smac mimetics because of an inability to form a ripoptosome complex.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Aug 29;4(8):e782. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.305. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23990022 Free PMC article.
-
Smac mimetics and TNFalpha: a dangerous liaison?Cell. 2007 Nov 16;131(4):655-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.042. Cell. 2007. PMID: 18022360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small-molecule SMAC mimetics as new cancer therapeutics.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Oct;144(1):82-95. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.05.007. Epub 2014 May 16. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24841289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune responses elicited by ssRNA(-) oncolytic viruses in the host and in the tumor microenvironment.J Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2023;9:10. doi: 10.20517/2394-4722.2022.92. Epub 2023 Apr 4. J Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2023. PMID: 37974615 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic identification of molecular subtype-selective vulnerabilities in non-small-cell lung cancer.Cell. 2013 Oct 24;155(3):552-66. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.09.041. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Cell. 2013. PMID: 24243015 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed necrosis in the cross talk of cell death and inflammation.Annu Rev Immunol. 2015;33:79-106. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112248. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Annu Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25493335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of programmed cell death by Brd4.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Dec 20;13(12):1059. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05505-1. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36539410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting apoptotic caspases in cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020 Jun;1867(6):118688. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118688. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32087180 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sawyers CL. Rational therapeutic intervention in cancer: Kinases as drug targets. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002;12:111–115. - PubMed
-
- Nachmias B, Ashhab Y, Ben-Yehuda D. The inhibitor of apoptosis protein family (IAPs): An emerging therapeutic target in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2004;14:231–243. - PubMed
-
- Liu Z, et al. Structural basis for binding of Smac/DIABLO to the XIAP BIR3 domain. Nature. 2000;408:1004–1008. - PubMed
-
- Srinivasula SM, et al. A conserved XIAP-interaction motif in caspase-9 and Smac/DIABLO regulates caspase activity and apoptosis. Nature. 2001;410:112–116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

