CD4 T-cell help programs a change in CD8 T-cell function enabling effective long-term control of murine gammaherpesvirus 68: role of PD-1-PD-L1 interactions
- PMID: 20534854
- PMCID: PMC2916546
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00784-10
CD4 T-cell help programs a change in CD8 T-cell function enabling effective long-term control of murine gammaherpesvirus 68: role of PD-1-PD-L1 interactions
Abstract
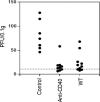
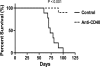
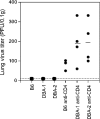
We previously showed that agonistic antibodies to CD40 could substitute for CD4 T-cell help and prevent reactivation of murine gammaherpesvirus 68 (MHV-68) in the lungs of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II(-/-) (CII(-/-)) mice, which are CD4 T cell deficient. Although CD8 T cells were required for this effect, no change in their activity was detected in vitro. A key question was whether anti-CD40 treatment (or CD4 T-cell help) changed the function of CD8 T cells or another cell type in vivo. To address this question, in the present study, we showed that adoptive transfer of CD8 T cells from virus-infected wild-type mice or anti-CD40-treated CII(-/-) mice caused a significant reduction in lung viral titers, in contrast to those from control CII(-/-) mice. Anti-CD40 treatment also greatly prolonged survival of infected CII(-/-) mice. This confirms that costimulatory signals cause a change in CD8 T cells enabling them to maintain effective long-term control of MHV-68. We investigated the nature of this change and found that expression of the inhibitory receptor PD-1 was significantly increased on CD8 T cells in the lungs of MHV-68-infected CII(-/-), CD40(-/-), or CD80/86(-/-) mice, compared with that in wild-type or CD28/CTLA4(-/-) mice, correlating with the level of viral reactivation. Furthermore, blocking PD-1-PD-L1 interactions significantly reduced viral reactivation in CD4 T-cell-deficient mice. In contrast, the absence of another inhibitory receptor, NKG2A, had no effect. These data suggest that CD4 T-cell help programs a change in CD8 T-cell function mediated by altered PD-1 expression, which enables effective long-term control of MHV-68.
Figures
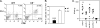
Similar articles
-
Insights into CD8 T Cell Activation and Exhaustion from a Mouse Gammaherpesvirus Model.Viral Immunol. 2020 Apr;33(3):215-224. doi: 10.1089/vim.2019.0183. Viral Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32286179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD40 engagement on dendritic cells, but not on B or T cells, is required for long-term control of murine gammaherpesvirus 68.J Virol. 2008 Nov;82(22):11016-22. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00919-08. Epub 2008 Sep 3. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18768977 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the role of negative T cell costimulatory pathways in CD4 and CD8 T cell-mediated alloimmune responses in vivo.J Immunol. 2005 Jun 1;174(11):6648-56. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.11.6648. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15905503
-
Induction of CD4 T cell changes in murine AIDS is dependent on costimulation and involves a dysregulation of homeostasis.J Immunol. 2002 Jul 15;169(2):722-31. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.2.722. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12097374
-
The role of CD40 ligand in costimulation and T-cell activation.Immunol Rev. 1996 Oct;153:85-106. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1996.tb00921.x. Immunol Rev. 1996. PMID: 9010720 Review.
Cited by
-
Suppressive CD8+ T cells arise in the absence of CD4 help and compromise control of persistent virus.J Immunol. 2011 Jun 1;186(11):6218-26. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003812. Epub 2011 Apr 29. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21531895 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into CD8 T Cell Activation and Exhaustion from a Mouse Gammaherpesvirus Model.Viral Immunol. 2020 Apr;33(3):215-224. doi: 10.1089/vim.2019.0183. Viral Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32286179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD4 T cell responses in latent and chronic viral infections.Front Immunol. 2013 May 13;4:105. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00105. eCollection 2013. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23717308 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of CD8 T cells accelerates anti-PD-1 antibody-induced psoriasis-like dermatitis through IL-6.Commun Biol. 2020 Oct 15;3(1):571. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01308-2. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 33060784 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Toxoplasma reactivation by rescue of dysfunctional CD8+ T-cell response via PD-1-PDL-1 blockade.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 May 31;108(22):9196-201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015298108. Epub 2011 May 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21576466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allan, W., Z. Tabi, A. Cleary, and P. C. Doherty. 1990. Cellular events in the lymph node and lung of mice with influenza. Consequences of depleting CD4+ T cells. J. Immunol. 144:3980-3986. - PubMed
-
- Barber, D. L., E. J. Wherry, D. Masopust, B. Zhu, J. P. Allison, A. H. Sharpe, G. J. Freeman, and R. Ahmed. 2006. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature 439:682-687. - PubMed
-
- Belz, G. T., H. Liu, S. Andreansky, P. C. Doherty, and P. G. Stevenson. 2003. Absence of a functional defect in CD8+ T cells during primary murine gammaherpesvirus-68 infection of I-A(b−/−) mice. J. Gen. Virol. 84:337-341. - PubMed
-
- Belz, G. T., P. G. Stevenson, M. R. Castrucci, J. D. Altman, and P. C. Doherty. 2000. Postexposure vaccination massively increases the prevalence of gamma-herpesvirus-specific CD8+ T cells but confers minimal survival advantage on CD4-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97:2725-2730. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

