Opal web services for biomedical applications
- PMID: 20529877
- PMCID: PMC2896135
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq503
Opal web services for biomedical applications
Abstract
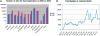
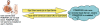
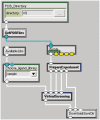
Biomedical applications have become increasingly complex, and they often require large-scale high-performance computing resources with a large number of processors and memory. The complexity of application deployment and the advances in cluster, grid and cloud computing require new modes of support for biomedical research. Scientific Software as a Service (sSaaS) enables scalable and transparent access to biomedical applications through simple standards-based Web interfaces. Towards this end, we built a production web server (http://ws.nbcr.net) in August 2007 to support the bioinformatics application called MEME. The server has grown since to include docking analysis with AutoDock and AutoDock Vina, electrostatic calculations using PDB2PQR and APBS, and off-target analysis using SMAP. All the applications on the servers are powered by Opal, a toolkit that allows users to wrap scientific applications easily as web services without any modification to the scientific codes, by writing simple XML configuration files. Opal allows both web forms-based access and programmatic access of all our applications. The Opal toolkit currently supports SOAP-based Web service access to a number of popular applications from the National Biomedical Computation Resource (NBCR) and affiliated collaborative and service projects. In addition, Opal's programmatic access capability allows our applications to be accessed through many workflow tools, including Vision, Kepler, Nimrod/K and VisTrails. From mid-August 2007 to the end of 2009, we have successfully executed 239,814 jobs. The number of successfully executed jobs more than doubled from 205 to 411 per day between 2008 and 2009. The Opal-enabled service model is useful for a wide range of applications. It provides for interoperation with other applications with Web Service interfaces, and allows application developers to focus on the scientific tool and workflow development. Web server availability: http://ws.nbcr.net.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Web servers and services for electrostatics calculations with APBS and PDB2PQR.J Comput Chem. 2011 May;32(7):1488-91. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21720. Epub 2011 Feb 1. J Comput Chem. 2011. PMID: 21425296 Free PMC article.
-
Biosphere: the interoperation of web services in microarray cluster analysis.Appl Bioinformatics. 2004;3(4):253-6. doi: 10.2165/00822942-200403040-00007. Appl Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15702956
-
A web services choreography scenario for interoperating bioinformatics applications.BMC Bioinformatics. 2004 Mar 10;5:25. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-25. BMC Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15113410 Free PMC article.
-
Web tools for predictive toxicology model building.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2012 Jul;8(7):791-801. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2012.685158. Epub 2012 May 12. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22577953 Review.
-
Evolution of web services in bioinformatics.Brief Bioinform. 2005 Jun;6(2):178-88. doi: 10.1093/bib/6.2.178. Brief Bioinform. 2005. PMID: 15975226 Review.
Cited by
-
AutoClickChem: click chemistry in silico.PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(3):e1002397. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002397. Epub 2012 Mar 15. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012. PMID: 22438795 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual interactomics of proteins from biochemical standpoint.Mol Biol Int. 2012;2012:976385. doi: 10.1155/2012/976385. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Mol Biol Int. 2012. PMID: 22928109 Free PMC article.
-
Tav4SB: integrating tools for analysis of kinetic models of biological systems.BMC Syst Biol. 2012 Apr 5;6:25. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-6-25. BMC Syst Biol. 2012. PMID: 22480273 Free PMC article.
-
metaXplor: an interactive viral and microbial metagenomic data manager.Gigascience. 2021 Feb 2;10(2):giab001. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giab001. Gigascience. 2021. PMID: 33527143 Free PMC article.
-
GO-Elite: a flexible solution for pathway and ontology over-representation.Bioinformatics. 2012 Aug 15;28(16):2209-10. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts366. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22743224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanner MF, Stoffler D, Olson AJ. ViPEr, a visual Programming Environment for Python. In Proceedings of thre 10th International Python conference. 2002 103-115. February 4-7, 2002. ISBN 1-930792-05-0.

