Identification of small molecules that suppress microRNA function and reverse tumorigenesis
- PMID: 20529860
- PMCID: PMC2915707
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.062976
Identification of small molecules that suppress microRNA function and reverse tumorigenesis
Abstract
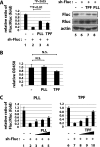
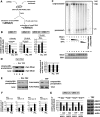
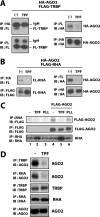
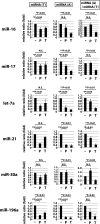
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) act in post-transcriptional gene silencing and are proposed to function in a wide spectrum of pathologies, including cancers and viral diseases. Currently, to our knowledge, no detailed mechanistic characterization of small molecules that interrupt miRNA pathways have been reported. In screening a small chemical library, we identified compounds that suppress RNA interference activity in cultured cells. Two compounds were characterized; one impaired Dicer activity while the other blocked small RNA-loading into an Argonaute 2 (AGO2) complex. We developed a cell-based model of miRNA-dependent tumorigenesis, and using this model, we observed that treatment of cells with either of the two compounds effectively neutralized tumor growth. These findings indicate that miRNA pathway-suppressing small molecules could potentially reverse tumorigenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Downregulation of Dicer enhances tumor cell proliferation and invasion.Int J Oncol. 2010 Aug;37(2):299-305. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000678. Int J Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20596657
-
MiRNA-192 [corrected] and miRNA-204 Directly Suppress lncRNA HOTTIP and Interrupt GLS1-Mediated Glutaminolysis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.PLoS Genet. 2015 Dec 28;11(12):e1005726. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005726. eCollection 2015 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26710269 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Northern blotting, precursor cloning, and Ago2-improved RNA interference.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;676:85-100. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-863-8_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 20931392
-
Dysregulation of microRNA biogenesis and gene silencing in cancer.Sci Signal. 2015 Mar 17;8(368):re3. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2005825. Sci Signal. 2015. PMID: 25783160 Review.
-
microRNA Therapeutics in Cancer - An Emerging Concept.EBioMedicine. 2016 Oct;12:34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.09.017. Epub 2016 Sep 20. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27720213 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miRNA: A Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 29;23(19):11502. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911502. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-guided screening strategy combining surface plasmon resonance with nuclear magnetic resonance for identification of small-molecule Argonaute 2 inhibitors.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 31;15(7):e0236710. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236710. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32735606 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecules with big roles in microRNA chemical biology and microRNA-targeted therapeutics.RNA Biol. 2019 Jun;16(6):707-718. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1593094. Epub 2019 Apr 3. RNA Biol. 2019. PMID: 30900502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulated MicroRNA Involvement in Multiple Sclerosis by Induction of T Helper 17 Cell Differentiation.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 4;9:1256. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01256. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29915595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA as an Important Target for Anticancer Drug Development.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 25;12:736323. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.736323. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34512363 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baltimore D., Boldin M. P., O'Connell R. M., Rao D. S., Taganov K. D. (2008) Nat. Immunol. 9, 839–845 - PubMed
-
- Garofalo M., Condorelli G., Croce C. M. (2008) Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 8, 661–667 - PubMed
-
- Soifer H. S., Rossi J. J., Saetrom P. (2007) Mol. Ther. 15, 2070–2079 - PubMed
-
- Grishok A., Pasquinelli A. E., Conte D., Li N., Parrish S., Ha I., Baillie D. L., Fire A., Ruvkun G., Mello C. C. (2001) Cell 106, 23–34 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

