Comparison of FcRn- and pIgR-mediated transport in MDCK cells by fluorescence confocal microscopy
- PMID: 20525015
- PMCID: PMC2975666
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01083.x
Comparison of FcRn- and pIgR-mediated transport in MDCK cells by fluorescence confocal microscopy
Abstract
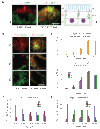
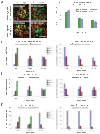
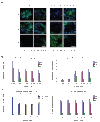
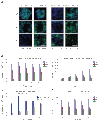
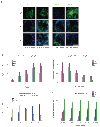
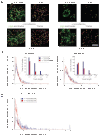
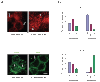
Protein delivery across polarized epithelia is controlled by receptor-mediated transcytosis. Many studies have examined basolateral-to-apical trafficking of polymeric IgA (pIgA) by the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR). Less is known about apical-to-basolateral transcytosis, the direction the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) transports maternal IgGs across intestinal epithelia. To compare apical-to-basolateral and basolateral-to-apical transcytosis, we co-expressed FcRn and pIgR in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells and used pulse-chase experiments with confocal microscopy to examine transport of apically applied IgG Fcgamma and basolaterally applied pIgA. Fcgamma and pIgA trafficking routes were initially separate but intermixed at later chase times. Fcgamma was first localized near the apical surface, but became more equally distributed across the cell, consistent with concomitant transcytosis and recycling. By contrast, pIgA transport was strongly unidirectional: pIgA shifted from near the basolateral surface to an apical location with increasing time. Some Fcgamma and pIgA fluorescence colocalized in early (EEA1-positive), recycling (Rab11a-positive), and transferrin (Tf)-positive common/basolateral recycling endosomes. Fcgamma became more enriched in Tf-positive endosomes with time, whereas pIgA was sorted from these compartments. Live-cell imaging revealed that vesicles containing Fcgamma or pIgA shared similar mobility characteristics and were equivalently affected by depolymerizing microtubules, indicating that both trafficking routes depended to roughly the same extent on intact microtubules.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Basolateral to apical transcytosis in polarized cells is indirect and involves BFA and trimeric G protein sensitive passage through the apical endosome.J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):83-100. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.83. J Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 7905002 Free PMC article.
-
Rab11-FIP1 and Rab11-FIP5 Regulate pIgR/pIgA Transcytosis through TRIM21-Mediated Polyubiquitination.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 28;22(19):10466. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910466. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638806 Free PMC article.
-
Polymeric IgA binding to the human pIgR elicits intracellular signalling, but fails to stimulate pIgR-transcytosis.Scand J Immunol. 2001 Jan;53(1):56-64. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.2001.00843.x. Scand J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11169207
-
Role of Polymeric Immunoglobulin Receptor in IgA and IgM Transcytosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 25;22(5):2284. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052284. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33668983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel functions of the polymeric Ig receptor: well beyond transport of immunoglobulins.Trends Immunol. 2003 Feb;24(2):55-8. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4906(02)00031-5. Trends Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12547499 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery and characterization of single-domain antibodies for polymeric Ig receptor-mediated mucosal delivery of biologics.MAbs. 2020 Jan-Dec;12(1):1708030. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2019.1708030. MAbs. 2020. PMID: 31906797 Free PMC article.
-
Cholix protein domain I functions as a carrier element for efficient apical to basal epithelial transcytosis.Tissue Barriers. 2020;8(1):1710429. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2019.1710429. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Tissue Barriers. 2020. PMID: 31928299 Free PMC article.
-
Albumin uptake and processing by the proximal tubule: physiological, pathological, and therapeutic implications.Physiol Rev. 2022 Oct 1;102(4):1625-1667. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00014.2021. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Physiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35378997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing IgG distribution to lung mucosal tissue improves protective effect of anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa antibodies.JCI Insight. 2018 Jun 21;3(12):e97844. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.97844. eCollection 2018 Jun 21. JCI Insight. 2018. PMID: 29925682 Free PMC article.
-
M Cells: Intelligent Engineering of Mucosal Immune Surveillance.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 2;10:1499. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01499. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31312204 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Simons K, Fuller SD. Cell surface polarity in epithelia. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:243–288. - PubMed
-
- Cereijido M, Ponce A, Gonzalezmariscal L. Tight junctions and apical basolateral polarity. J Membr Biol. 1989;110:1–9.
-
- Mostov KE. Transepithelial transport of immunoglobulins. Ann Rev Immunol. 1994;12:63–84. - PubMed
-
- Brandtzaeg P, Prydz H. Direct evidence for an integrated function of J-chain and secretory component in epithelial transport of immunoglobulins. Nature. 1984;311:71–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

