Role of noncovalent SUMO binding by the human cytomegalovirus IE2 transactivator in lytic growth
- PMID: 20519406
- PMCID: PMC2916544
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00459-10
Role of noncovalent SUMO binding by the human cytomegalovirus IE2 transactivator in lytic growth
Abstract
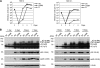
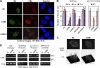
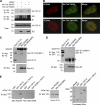
The 86-kDa immediate-early 2 (IE2) protein of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is a promiscuous transactivator essential for viral gene expression. IE2 is covalently modified by SUMO at two lysine residues (K175 and K180) and also interacts noncovalently with SUMO. Although SUMOylation of IE2 has been shown to enhance its transactivation activity, the role of SUMO binding is not clear. Here we showed that SUMO binding by IE2 is necessary for its efficient transactivation function and for viral growth. IE2 bound physically to SUMO-1 through a SUMO-interacting motif (SIM). Mutations in SIM (mSIM) or in both SUMOylation sites and SIM (KR/mSIM), significantly reduced IE2 transactivation effects on viral early promoters. The replication of IE2 SIM mutant viruses (mSIM or KR/mSIM) was severely depressed in normal human fibroblasts. Analysis of viral growth curves revealed that the replication defect of the mSIM virus correlated with low-level accumulation of SUMO-modified IE2 and of viral early and late proteins. Importantly, both the formation of viral transcription domains and the association of IE2 with viral promoters in infected cells were significantly reduced in IE2 SIM mutant virus infection. Furthermore, IE2 was found to interact with the SUMO-modified form of TATA-binding protein (TBP)-associated factor 12 (TAF12), a component of the TFIID complex, in a SIM-dependent manner, and this interaction enhanced the transactivation activity of IE2. Our data demonstrate that the interaction of IE2 with SUMO-modified proteins plays an important role for the progression of the HCMV lytic cycle, and they suggest a novel viral mechanism utilizing the cellular SUMO system.
Figures
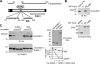





Similar articles
-
Casein kinase-2-mediated phosphorylation increases the SUMO-dependent activity of the cytomegalovirus transactivator IE2.J Biol Chem. 2019 Oct 4;294(40):14546-14561. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009601. Epub 2019 Aug 1. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31371453 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of interactions of human cytomegalovirus immediate-early IE2 regulatory protein with small ubiquitin-like modifiers and their conjugation enzyme Ubc9.J Virol. 2001 Apr;75(8):3859-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.8.3859-3872.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11264375 Free PMC article.
-
Covalent modification of the transactivator protein IE2-p86 of human cytomegalovirus by conjugation to the ubiquitin-homologous proteins SUMO-1 and hSMT3b.J Virol. 2000 Mar;74(6):2510-24. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.6.2510-2524.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10684265 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of covalent and noncovalent SUMO interactions with the major human cytomegalovirus transactivator IE2p86 for viral infection.J Virol. 2009 Dec;83(24):12881-94. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01525-09. Epub 2009 Oct 7. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19812159 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation of the human cytomegalovirus 72-kilodalton IE1 protein facilitates expression of the 86-kilodalton IE2 protein and promotes viral replication.J Virol. 2004 Jul;78(14):7803-12. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.14.7803-7812.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15220454 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Insights into the Transcriptome of Human Cytomegalovirus: A Comprehensive Review.Viruses. 2023 Aug 8;15(8):1703. doi: 10.3390/v15081703. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37632045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus IE2 Both Activates and Represses Initiation and Modulates Elongation in a Context-Dependent Manner.mBio. 2022 Jun 28;13(3):e0033722. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00337-22. Epub 2022 May 17. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35579393 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-host protein interactions as footprints of human cytomegalovirus replication.Curr Opin Virol. 2022 Feb;52:135-147. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2021.11.016. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Curr Opin Virol. 2022. PMID: 34923282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site-specific SUMOylation of viral polymerase processivity factor: a way of localizingtoND10 subnuclear domains for restricted and self-controlled reproduction of herpesvirus.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):2883-2901. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.2000689. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 34747321 Free PMC article.
-
Non-covalent Interaction With SUMO Enhances the Activity of Human Cytomegalovirus Protein IE1.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 13;9:662522. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.662522. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34055792 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn, J. H., C. J. Chiou, and G. S. Hayward. 1998. Evaluation and mapping of the DNA binding and oligomerization domains of the IE2 regulatory protein of human cytomegalovirus using yeast one and two hybrid interaction assays. Gene 210:25-36. - PubMed
-
- Ahn, J. H., and G. S. Hayward. 2000. Disruption of PML-associated nuclear bodies by IE1 correlates with efficient early stages of viral gene expression and DNA replication in human cytomegalovirus infection. Virology 274:39-55. - PubMed
-
- Ahn, J. H., W. J. Jang, and G. S. Hayward. 1999. The human cytomegalovirus IE2 and UL112-113 proteins accumulate in viral DNA replication compartments that initiate from the periphery of promyelocytic leukemia protein-associated nuclear bodies (PODs or ND10). J. Virol. 73:10458-10471. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

