Measurement and identification of S-glutathiolated proteins
- PMID: 20513478
- PMCID: PMC3142817
- DOI: 10.1016/S0076-6879(10)73009-3
Measurement and identification of S-glutathiolated proteins
Abstract
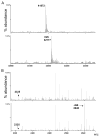
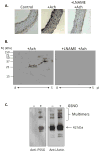
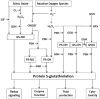
Protein thiol modifications occur under both physiological and pathological conditions and can regulate protein function, redox signaling, and cell viability. The thiolation of proteins by glutathione (GSH) appears to be a particularly important mode of posttranslational modification that is increased under conditions of oxidative or nitrosative stress. Modification of proteins by glutathiolation has been shown to affect the structure and function of several susceptible proteins and protect them from subsequent oxidative injury. In many cases, the glutathiolated proteins are low in abundance, and dethiolation occurs readily. Therefore, sensitive, reliable, and reproducible methods are required for measuring both the total levels of protein glutathiolation and for identifying glutathiolated proteins under given conditions. These methods necessitate the preservation or the controlled removal of the GSH adducts during sample preparation for the accurate measurement of total S-glutathiolation and for the identification of protein-GSH adducts. In this chapter, we briefly review and provide protocols for chemical, mass spectrometric, immunological, and radioactive tagging techniques, for measuring protein S-glutathiolation in cells and tissues.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigating protein thiol chemistry associated with dehydroascorbate, homocysteine and glutathione using mass spectrometry.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2020 Jun 15;34(11):e8774. doi: 10.1002/rcm.8774. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2020. PMID: 32119756
-
Irreversible thiol oxidation in carbonic anhydrase III: protection by S-glutathiolation and detection in aging rats.Biol Chem. 2002 Mar-Apr;383(3-4):649-62. doi: 10.1515/BC.2002.067. Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12033454
-
Role of glutathiolation in preservation, restoration and regulation of protein function.IUBMB Life. 2007 Jan;59(1):21-6. doi: 10.1080/15216540701196944. IUBMB Life. 2007. PMID: 17365176 Review.
-
Protein S-glutathiolation: redox-sensitive regulation of protein function.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012 Mar;52(3):559-67. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.07.009. Epub 2011 Jul 20. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 21784079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein glutathiolation by nitric oxide: an intracellular mechanism regulating redox protein modification.FASEB J. 2006 Aug;20(10):1715-7. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-5843fje. Epub 2006 Jun 29. FASEB J. 2006. PMID: 16809435
Cited by
-
Gbb glutathionylation promotes its proteasome-mediated degradation to inhibit synapse growth.J Cell Biol. 2023 Sep 4;222(9):e202202068. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202202068. Epub 2023 Jun 30. J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37389657 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Montelukast on Liver Damage in an Experimental Obstructive Jaundice Model.Viszeralmedizin. 2015 Apr;31(2):131-8. doi: 10.1159/000375434. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Viszeralmedizin. 2015. PMID: 26989383 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of External NADPH Dehydrogenase-NDB1 in Arabidopsis thaliana Confers Improved Tolerance to Ammonium Toxicity via Efficient Glutathione/Redox Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 9;19(5):1412. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051412. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29747392 Free PMC article.
-
Dysfunctional mitochondrial bioenergetics and oxidative stress in Akita(+/Ins2)-derived β-cells.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Sep 1;305(5):E585-99. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00093.2013. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23820623 Free PMC article.
-
Sortase-mediated segmental labeling: A method for segmental assignment of intrinsically disordered regions in proteins.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 28;16(10):e0258531. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258531. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34710113 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adachi T, Weisbrod RM, Pimentel DR, Ying J, Sharov VS, Schoneich C, Cohen RA. S-Glutathiolation by peroxynitrite activates SERCA during arterial relaxation by nitric oxide. Nat Med. 2004;10:1200–1207. - PubMed
-
- Biswas S, Chida AS, Rahman I. Redox modifications of protein-thiols: emerging roles in cell signaling. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;71:551–564. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P20 RR024489/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059378/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-78825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- GM71036/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL078825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-59378/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071036-06/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK036118/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK036118/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR-024489/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 DK036118/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055477-14/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059378-13/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-55477/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK036118-24/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055477/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071036/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

